Table of Contents
ToggleHuman Resources Management (HRM), is the recognition of the employees’ values, Starting with recruiting, hiring, training, compensating, retaining, and motivating employees, To the organization of the current employees’ mission and goals. HR Management is about understanding people: their strengths, aspirations, and how best to align these with the organization’s goals. HRM develops policies that help ensure employees safety.
The methodology behind HRM recognizes the valued employees bring to an organization, also known as human capital.
Human capital management (HCM), is becoming increasingly important, especially as many roles are automated. With more employees working remotely and increased specialized skills and workforce data,
HCM teams and managers can offer comprehensive support across an organization and bring out the best in everyone.
Investing in employees and supporting their needs can improve employees’ satisfaction and motivation. Employees who are well trained, valued, and supported by their employers will likely have the skills and incentive necessary to carry out the organization’s goals.
1.Recruitment
The HRM plays a role in the recruitment process, acting as the backbone of sourcing, attracting, selecting, and onboarding new employees. The recruitment process is critical for acquiring the right talent that aligns with the organization’s culture and goals.
Defining Job Requirements
- Job Analysis: HR conducts a thorough job analysis to understand the responsibilities, necessary skills, and qualifications required for the role. This helps in creating accurate job descriptions and specifications.
- Job Descriptions: Crafting clear and concise job descriptions that outline the role’s responsibilities, required qualifications, skills, and competencies. This is crucial for attracting suitable candidates.
Sourcing Candidates
- Developing a Sourcing Strategy: HR identifies the most effective sourcing strategies for the role, which may include online job postings, social media, employee referrals, recruitment agencies, and job fairs.
- Building a Talent Pool: HR works on building a pool of potential candidates for current and future opportunities through networking, talent scouting, and maintaining relationships with past applicants.
Screening and Selection
- Application Screening: HR screens applications and resumes to identify candidates who meet the minimum qualifications and possess the desired skills and experience.
- Interviewing: Conducting initial interviews to further assess candidates’ qualifications, cultural fit, and potential for the role. HR may also coordinate interviews with the hiring manager and other relevant team members.
- Assessment: HR may administer tests or assessments to evaluate candidates’ skills, competencies, and fit for the organization’s culture and values.
Offering Employment
- Reference and Background Checks: Verifying the selected candidate’s references, background, and any other checks required for the role to ensure credibility and reliability.
- Job Offers: HR prepares and extends job offers, including salary negotiations, benefits, and other terms of employment, ensuring that offers are competitive and in line with organizational policies.
Onboarding
- Orientation: HR coordinates the orientation process, introducing new hires to the organization’s culture, policies, and procedures.
- Integration: Facilitating the integration of new employees into their teams, including setting up necessary tools and systems, and ensuring they have the resources needed to succeed in their roles.

2.Develop Employees’ Skills.
The HRM plays a pivotal role in developing employees’ skills, to ensure that the workforce is prepared and capable of meeting current and future organizational challenges. This involves:
- Skill Gaps: HR can conduct assessments and use performance reviews to identify the current skills of employees and know where there are gaps.
- Development Plans: For effective skill development, HR should work with employees and their managers to create personalized development plans. These plans should consider the employee’s career aspirations, the skills they need to develop to achieve their goals, and the skills the organization needs.
- Training and Learning Opportunities: HR is responsible for organizing training sessions, workshops, and seminars that are aligned with the identified skill gaps. This could include bringing in external trainers, developing training programs, or facilitating access to online courses and certifications.
- Technology for Learning: Technological tools can make learning more accessible and flexible. HR can curate a library of resources that employees can access to develop their skills at their own pace.
- Measuring Outcomes: It’s important for HR to track the effectiveness of training and development programs. This can be done through feedback surveys, assessments, and by measuring changes in performance and productivity.
- Skill Development with Performance Management: Skill development should be a continuous process, integrated with performance management. HR should ensure that performance reviews include discussions about skill development and future learning goals.
- Collaborative Learning: Encouraging teamwork and collaborative projects can lead to skill sharing and development. HR can facilitate cross-functional teams or projects that allow employees to learn from one another.
3.Workplace Culture
The HRM has a strong focus on company culture and job satisfaction. Much of what motivates employees comes from the culture in which they work. HR can create an environment where employees feel motivated, supported, and aligned with the organizational goals, driving success and sustainability.
- Organizational Values: HR is defining and communicating the values and mission of the organization. These values should guide behaviors and decision making processes, creating a vision that employees can rally around.
- Open Communication: A productive workplace culture, HR can facilitate this by implementing policies that encourage open dialogue between employees and management, providing platforms for feedback, and ensuring that communication is two-way and effective.
- Recognition and Reward Systems: Recognizing and rewarding employees for their contributions is crucial for motivation and engagement. HR can design and manage recognition programs that align with organizational goals, ensuring employees feel appreciated for their hard work and dedication.
- Fostering Employee Well-being: HR must prioritize the physical and mental well-being of employees. This includes implementing wellness programs, ensuring work-life balance, and providing support for mental health. A healthy workforce is a more productive one.
4.Protect Employees
The HRM plays a role in protecting employees, aim to safeguarding the well-being, rights, and dignity of employees within an organization. HRM creates a safe, healthy, and equitable work environment, which is essential for employees’ satisfaction, retention, and productivity.
Safe Work Environment
- Physical Safety: Implementing and enforcing safety standards, conducting regular safety audits, and providing training to prevent workplace accidents and injuries.
- Psychological Safety: Promoting a culture where employees feel valued and supported, can express their opinions without fear of retribution, and can report concerns knowing they will be taken seriously.
Legal Compliance
- Equal Employment Opportunity: anti-discrimination policies to ensure all employees have equal access to opportunities and are treated fairly, regardless of race, gender, age, religion, or other protected characteristics.
Employee Privacy
- Confidentiality of Personal Information: Safeguarding sensitive employee information, such as personal data, health records, and financial information, against unauthorized access or disclosure.
Health and Well-being
- Mental Health Support: Providing resources and support for mental health, such as employee assistance programs, counseling services, and stress management workshops.
- Work-Life Balance: Encouraging policies and practices that support a healthy work-life balance, including flexible working hours, remote work options, and generous leave policies.
5.Work-Life Balance
The HRM plays a role in work-life balance within an organization. Work-life balance refers to the equilibrium between professional work and personal life,
allowing employees to feel fulfilled in both without one overwhelming the other. This balance is crucial for maintaining employee well-being, satisfaction, and productivity. HR departments can implement various policies to support this balance, highlighting their essential role in fostering a supportive work environment.
Flexible Work Arrangements
- Flexible Hours: Allowing employees to choose their working hours within certain limits can help them manage personal responsibilities alongside professional duties.
- Remote Work: Offering options to work from home or other locations provides employees with the flexibility to create work environments that suit their personal life better.
- Compressed Workweeks: Implementing four-day workweeks or similar arrangements can give employees longer periods of rest and personal time.
Leave Policies
- Paid Time Off (PTO): Encouraging the use of PTO for vacations, personal days, or mental health breaks helps employees recharge and reduce burnout.
- Parental Leave: Providing comprehensive maternity, paternity, and adoption leave supports new parents in balancing family expansion with career responsibilities.
Day Off: is the 1st tracker for team’s PTO, vacations and absences, were HR use to save the time spent on tracking the team’s vacations, Day Off will help you track your team’s leaves and absences in one place. In seconds you will set up your leave policies, approval workflow and enjoy a unique experience.
Day Off
- You can add unlimited numbers of employees.
- Supports various leave types (e.g., annual, sick, maternity/paternity leave) and Supports Days and Hours balance, you can add unlimited numbers of leave types and leave policies.
- You can Customize week starting day settings according to your company’s operational days.
- Setting up public holidays specific to your country or region, by importing holidays from Google.
- The app can integrate with ( Slack, Google Calendar, Outlook Calendar and Teams)
- Supports Accruals & Carry overs.
Before Leave tracking systems HR were adding the annual PTO balances manually, using Excel template as below:
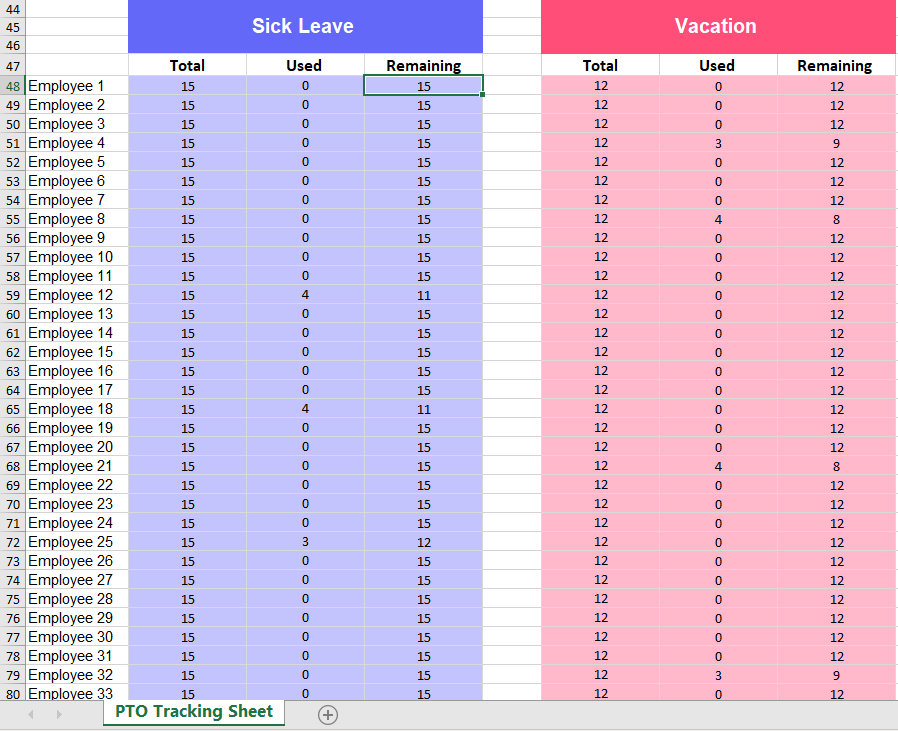
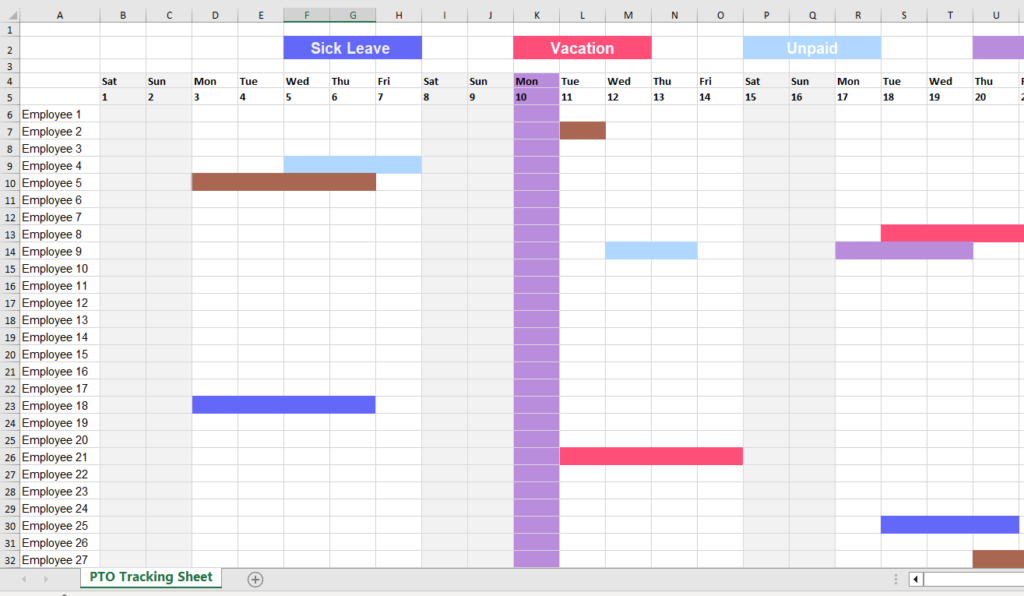
And track the dates the each employee will be taking time off, also by using excel as the below.
6.Payroll Management
The HRM plays a critical role in the administration and management of payroll, Payroll management involves more than just ensuring employees are paid accurately and on time, it encompasses a range of activities from maintaining employee records, ensuring compliance with tax laws, to contributing to employee satisfaction and morale.
Accurate and Timely Payment
- Data Management: HRM is responsible for collecting, verifying, and managing employee information that affects payroll, including hours worked, pay rates, deductions, and benefits enrollment.
- Payroll Processing: HRM either directly processes payroll or works closely with the finance department or an external payroll service provider to ensure employees receive their paychecks accurately and on time.
Compliance with Laws and Regulations
- Tax Compliance: HRM ensures compliance with state, and local tax laws, including the accurate calculation and withholding of taxes from employee paychecks.
- Reporting Requirements: HRM is responsible for the timely submission of payroll-related reports to government agencies, such as tax filings and contributions to social security.
- Labor Laws: Compliance with labor laws, including minimum wage, overtime, and working hours regulations, is managed by HRM to ensure legal compliance and to protect the organization from potential lawsuits and penalties.
Record Keeping and Information Management
- Confidentiality and Security: HRM ensures the confidentiality and security of payroll information, protecting sensitive employee data from unauthorized access.
- Record Keeping: HRM maintains comprehensive payroll records for each employee, including historical pay records, deductions, and hours worked, in compliance with legal requirements.
Integration with HR Functions
- Performance Management: HRM integrates payroll with performance management systems, where pay raises, bonuses, and incentives are aligned with performance evaluations.
- Onboarding and Offboarding: HRM ensures that payroll processes are seamlessly integrated with employee onboarding and offboarding, managing aspects like final paychecks and deductions.
7.Careers in Hr Management
You can find many different careers in HRM, with different points of entry into this field. Most positions in HRM require a bachelor’s degree in human resources or a related field. You can also earn certifications to help you find the best position within HRM field. HRM professionals have important jobs that can be both rewarding and fulfilling.
HR Generalist
HR Generalists are handling a wide range of responsibilities from recruiting, onboarding, benefits administration, to employee relations. They may work in small to medium sized enterprises or as part of a larger HR team in big corporations.
Recruitment and Talent Acquisition Specialist
These specialists focus on attracting and hiring talent. Their responsibilities include posting job ads, screening candidates, conducting interviews, and working on employer branding strategies. They play a crucial role in ensuring that the organization attracts and retains high-quality talent.
Training and Development Manager
These managers are responsible for designing and implementing training programs to enhance employee skills and knowledge. This role involves assessing training needs, facilitating workshops, and evaluating the effectiveness of training programs.
Employee Relations Manager
This role involves developing and maintaining a positive work environment. Employee Relations Managers address mediate disputes, and ensure compliance with labor laws. They also work on policies that promote diversity, equity, and inclusion
8.Gain HR experience.
The field of HRM is constantly evolving with the integration of technology and changes in the workforce. Professionals in this field need to be adaptable, have excellent interpersonal skills, and a strong understanding of business operations and strategy.
One way to get experience is through internships and entry-level positions such as human resources assistant or associate. In these entry-level roles, you’ll assist in the major duties of HR and build experience to move forward. Joining professional organizations and attending networking opportunities like conferences and conventions is another way to gain experience, knowledge, and connections in HRM.
Read more: How to Use LinkedIn: A Guide to Online Networking
Conclusion
To Have a career in HRM, individuals typically need a bachelor’s degree in human resources, business administration, or a related field. Many roles, especially at higher levels, may require a master’s degree in human resources management. Professional certifications, such as those offered by the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) or the HR Certification Institute (HRCI), can also enhance job prospects and career advancement opportunities.
