Table of Contents
TogglePaid Time Off (PTO) is a key benefit many employers offer that allows employees to take time away from work while still receiving compensation. Whether for vacations, personal days, or sick leave, knowing how to calculate the PTO accrual rate is essential for employers and employees. Understanding this process ensures transparency, enables better planning, and fosters a fair working environment. In this article, we will delve into what PTO accrual is, how to calculate it, and the various methods employers can use to determine the accrual rate for their workforce.
What is PTO Accrual?
PTO accrual refers to the method by which employees earn paid time off over time, usually based on the number of hours they work. Rather than receiving a lump sum of vacation days at the start of the year, employees often accrue PTO gradually, accumulating hours or days as they continue to work. This system is particularly common in businesses where employees are paid hourly or work irregular hours, but it is also used in salaried positions.
There are various ways to calculate PTO accrual, and the chosen method often depends on the company’s policies, employment contracts, and legal requirements. Here, we’ll explore different approaches to calculating PTO accrual rate and provide detailed steps for each method.
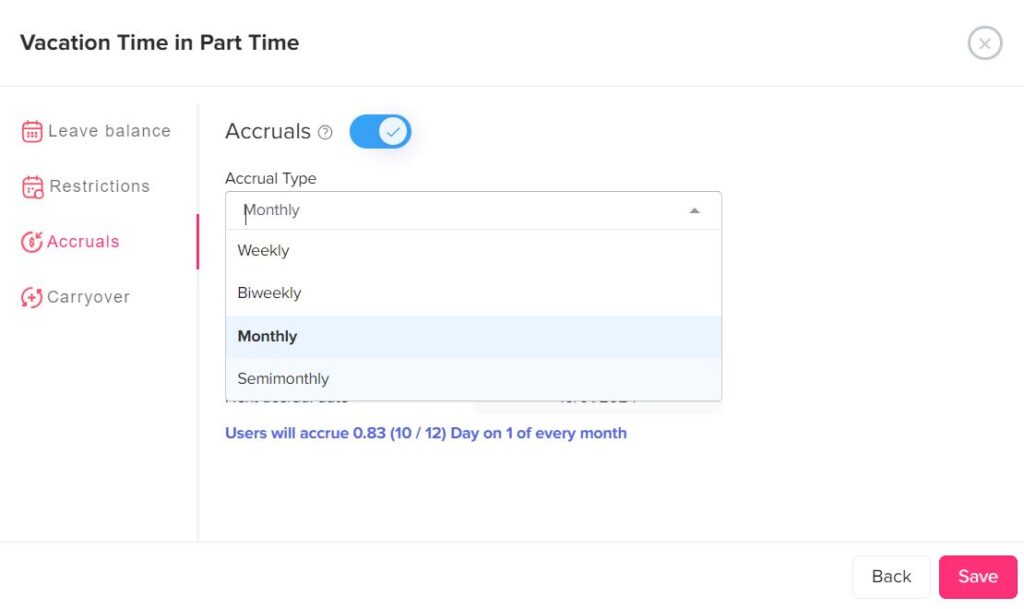
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating PTO Accrual Rate
Determine the Total PTO Offered Per Year
The first step in calculating the PTO accrual rate is knowing how much PTO employees are entitled to over a year. This number is typically provided in company policies, employee handbooks, or contracts. For example, a company may offer 15 days of PTO per year, which is equivalent to 120 hours for employees who work 8-hour days.
Formula for full-time employees:
Total PTO (in hours) = PTO days per year × Hours per workday
Example: If an employee is entitled to 15 PTO days and works 8 hours per day:
Total PTO = 15 days × 8 hours = 120 hours of PTO per year
Determine the Accrual Period
Once you know how much PTO is offered annually, the next step is to figure out the period over which PTO will accrue. This period depends on how frequently the employee is paid. Common accrual periods include:
- Weekly
- Bi-weekly (every two weeks)
- Monthly
- Semimonthly
Most companies prefer to base PTO accrual on pay periods. For instance, if employees are paid bi-weekly, their PTO accrual will be divided by the number of pay periods in a year (26 in the case of bi-weekly payroll).
Example: If the employee accrues PTO bi-weekly, and the company has 26 pay periods in a year, the accrual rate would be:
PTO per pay period = Total annual PTO ÷ Number of pay periods
So, if an employee has 120 hours of PTO per year, the calculation would be:
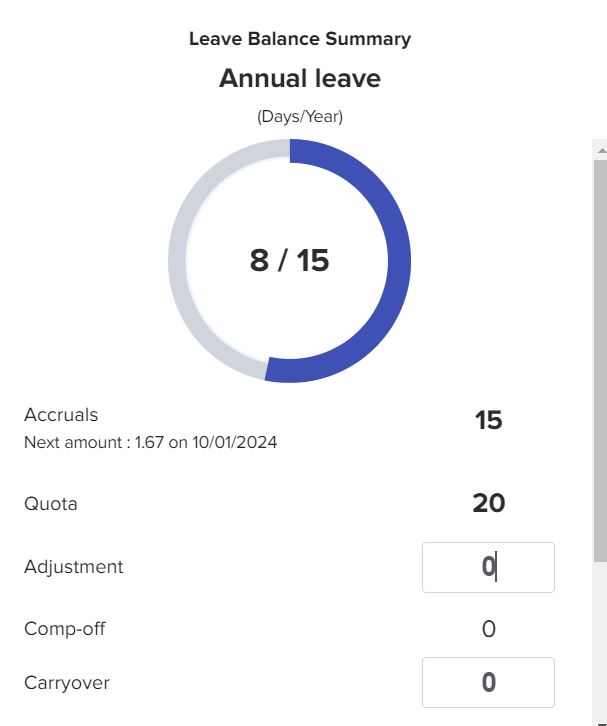
Calculate the Accrual Rate Based on Hours Worked
For hourly employees, PTO is typically accrued based on the number of hours worked. Employers use an accrual rate (hours of PTO earned per hour worked) to calculate this. To determine this accrual rate, divide the total annual PTO by the total number of work hours per year. In the U.S., a standard full-time employee typically works 2080 hours per year (40 hours per week × 52 weeks).
Formula: Accrual rate per hour = Total PTO hours per year ÷ Total work hours per year
Example: If an employee earns 120 hours of PTO per year and works 2080 hours annually:
Accrual rate = 120 hours ÷ 2080 hours = 0.0577 hours of PTO earned per hour worked
This means for every hour the employee works, they earn about 0.0577 hours of PTO. Over time, these small fractions accumulate to full hours and days of PTO.
Accruing PTO for Part-Time Employees
Part-time employees usually accrue PTO at a lower rate than full-time employees, based on the number of hours they work. The same formula for full-time employees applies, but with adjustments for the actual hours worked by part-time staff.
For example, if a part-time employee works 20 hours per week instead of 40, and the company offers the same 120 hours of PTO annually, the calculation would be based on the part-time employee’s actual hours.
Formula: Accrual rate = (Total annual PTO for full-time employees ÷ Total work hours for full-time employees) × Actual hours worked by part-time employee
Example: If the part-time employee works 1040 hours a year (20 hours per week), their accrual rate would be:
Accrual rate = (120 hours ÷ 2080 hours) × 1040 hours = 60 hours of PTO per year
Track PTO Accrual
Once the accrual rate is determined, the next crucial step is tracking the PTO over time. Most payroll systems or HR software can handle this automatically, ensuring that employees’ PTO is calculated based on their hours worked and the company’s specific accrual rules.
If tracking PTO manually, it’s important to ensure consistency in calculations, especially if the employee works varying hours. You can set up a spreadsheet to track each pay period’s accrual and total PTO.
Example: For a bi-weekly payroll, if an employee earns 4.62 hours of PTO per pay period (as calculated earlier), after 10 pay periods, the employee would have:
Total PTO accrued = 4.62 hours × 10 pay periods = 46.2 hours of PTO
Different Methods for PTO Accrual
Employers can choose from various methods to calculate PTO accrual based on company policy or legal requirements. Below are the most common methods:
Fixed Accrual (Per Pay Period)
This method divides the total PTO into equal parts that employees earn during each pay period. As described earlier, employees accrue a set number of hours each pay period, whether it’s weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly. This method is straightforward to implement.
PTO Bank (Lump Sum)
In some companies, PTO is provided as a lump sum at the beginning of the year. Instead of accruing over time, employees get their full PTO allowance upfront. This method simplifies PTO tracking but requires careful management to ensure employees do not exhaust their PTO too early in the year.
Anniversary-Based Accrual
Some companies calculate PTO accrual based on the employee’s work anniversary rather than the calendar year. Employees earn PTO based on their specific hire date, which resets each year on their anniversary.
Variable Accrual Rate
Some employers offer PTO that increases with tenure. For example, employees may earn 10 days of PTO in their first year and 15 days after three years of service. This incentivizes long-term employment and rewards loyalty. The calculation of accrual would be adjusted based on how long the employee has been with the company.
PTO Accrual Caps and Limits
It’s common for employers to set limits or caps on how much PTO an employee can accrue. This prevents employees from stockpiling excessive amounts of time off. Once an employee hits the accrual cap, they will stop earning additional PTO until they use some of their accrued time.
Example: If a company sets a cap at 160 hours of PTO, an employee who accrues 120 hours per year will stop accruing PTO once their balance reaches 160 hours. To start accruing again, the employee must take time off, reducing their balance below the cap.
Legal Considerations for PTO Accrual
While PTO policies are generally set by the employer, there are legal guidelines in some jurisdictions that govern how PTO is accrued, managed, and paid out upon termination. Employers should be aware of local labor laws regarding:
- Minimum PTO accrual requirements.
- Whether accrued PTO must be paid out upon an employee’s departure.
- Accrual caps and rollover rules.
Employers are responsible for ensuring that their PTO policies comply with relevant labor laws and that they are communicated clearly to employees.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About PTO Accrual
What does PTO stand for?
PTO stands for Paid Time Off, a benefit that allows employees to take time away from work while still receiving their regular pay. It usually covers vacation, sick leave, and personal time under a single policy.
How is PTO different from vacation time?
Vacation time is specifically meant for rest and holidays, while PTO is a broader system that also includes sick days and personal leave. PTO gives employees more flexibility in how they use their time off.
Do all employees accrue PTO?
Not necessarily. Whether an employee accrues PTO depends on the company’s policy, employment status, and local labor laws. Some organizations provide a lump sum of PTO at the beginning of the year instead of having employees earn it gradually.
How often is PTO updated?
PTO is typically updated according to the payroll cycle, which could be weekly, bi-weekly, semi-monthly, or monthly, depending on the employer’s practices.
Can part-time employees earn PTO?
Yes, part-time employees can earn PTO, but usually at a rate proportional to the number of hours they work compared to full-time employees.
What happens if PTO is not used?
This depends on the employer’s policy. Some allow unused PTO to roll over into the next year, some place limits on how much can be carried over, and others may have a “use it or lose it” rule where unused days expire.
Is unused PTO paid out when leaving a company?
In many places, accrued PTO is considered part of an employee’s earned wages and must be paid out upon resignation or termination. However, this can vary depending on local labor laws and company policy.
How can employees check their PTO balance?
Most companies provide access through HR or payroll software, where employees can log in and view their current PTO balance. If that’s not available, employees can usually request the information from HR or payroll directly.
Does PTO increase with length of service?
Many employers reward loyalty by increasing PTO entitlement as employees gain more years of service. This means the longer someone stays with the company, the more PTO they may be eligible to earn.
Can PTO be taken before it is accrued?
This depends on company policy. Some employers allow employees to borrow time in advance, resulting in a negative balance, while others require PTO to be fully accrued before it can be used.
Conclusion
Calculating PTO accrual may seem complex at first, but by breaking it down into clear steps and understanding the different methods available, employers and employees alike can manage and track PTO more effectively. The key factors to keep in mind include understanding the total PTO offered, determining the accrual period, calculating the accrual rate based on hours worked, and tracking it consistently.
Whether you’re a business owner setting up a PTO system or an employee trying to understand how much time off you’ve earned, understanding the mechanics of PTO accrual ensures transparency and fairness in the workplace. By using the right formulas and tools, both employers and employees can manage their time off efficiently, benefiting overall work-life balance.
