Table of Contents
TogglePTO management in hospitals and clinics requires far more strategic planning than in most industries. Healthcare facilities operate 24/7, depend on precise staffing ratios, and must maintain uninterrupted patient care. At the same time, healthcare professionals work in high stress environments where rest and recovery are essential to performance, safety, and retention.
PTO management in healthcare is not simply an administrative HR time off planning. It is a workforce planning strategy that directly impacts clinical quality, operational stability, staff morale, and financial performance.
Below is a comprehensive guide to implementing best practices for PTO management in hospitals and clinics.
Understanding the Unique Challenges of PTO in Healthcare
Before designing an effective PTO strategy, it is important to understand the unique pressures healthcare organizations face:
Continuous operations (24/7 coverage)
Mandatory nurse to patient ratios in many regions
Emergency unpredictability
High burnout rates among nurses and physicians
Rotating and overnight shifts
Compliance with labor laws and medical leave regulations
Specialized staff roles that are difficult to replace on short notice
Unlike traditional office roles where work can sometimes be redistributed, clinical responsibilities require qualified coverage at all times. One unplanned absence can create overtime costs, stress for remaining staff, and potential safety risks.
This makes proactive PTO planning essential.
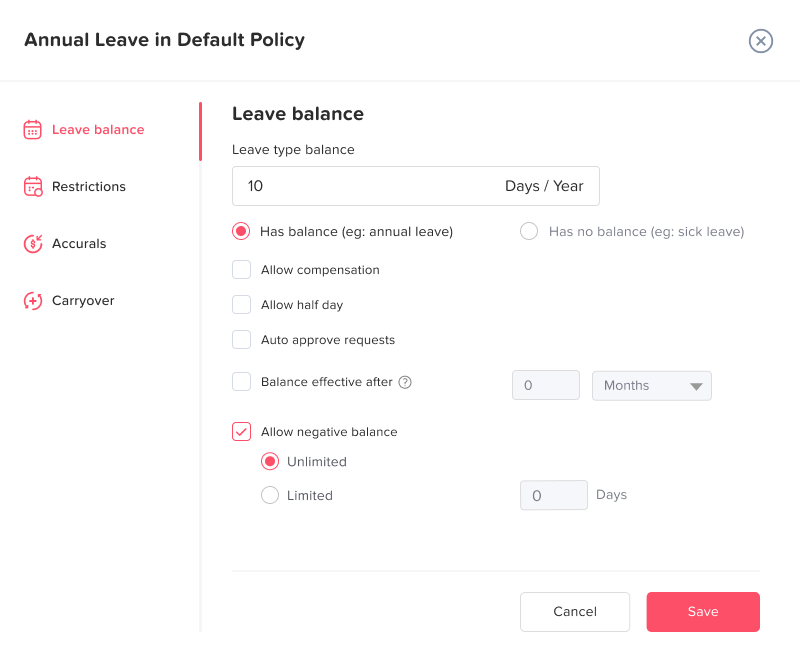
Build Clear, Detailed, and Accessible PTO Policies
Ambiguity in PTO policies creates conflict and frustration. In healthcare settings, clarity is even more critical because leave decisions can directly affect patient care.
A well structured PTO policy should clearly outline:
How PTO is accrued (per pay period, annually, per hour worked)
Differences between vacation, sick leave, emergency leave, and unpaid leave
Carryover rules and expiration limits
Notice requirements for planned leave
Approval authority levels (manager, HR, department head)
Blackout periods
Shift swap rules
Procedures for sudden illness or family emergencies
Policies should be written in plain language and easily accessible via employee portals or internal systems. Transparency reduces misunderstandings and supports fairness across departments.
Additionally, policies should account for different employment types:
Full time staff
Part time employees
Per diem nurses
Contract physicians
Each category may require tailored accrual and eligibility rules.

Connect PTO Planning With Workforce Forecasting
In hospitals and clinics, PTO approval should never happen in isolation. Every request must be evaluated against staffing needs and patient demand projections.
Workforce forecasting involves:
Reviewing historical patient volume trends
Identifying seasonal surges (flu season, holidays)
Planning for known high demand periods
Maintaining minimum staffing ratios per unit
Anticipating physician or specialist availability
Advanced planning helps prevent last minute staffing crises.
Best practice includes implementing departmental PTO caps. For example:
Only a specific number of nurses per shift can be off
Certain critical roles cannot overlap on leave
Supervisory staff absences are staggered
This structured approach protects operations while still allowing staff to plan their time off fairly.
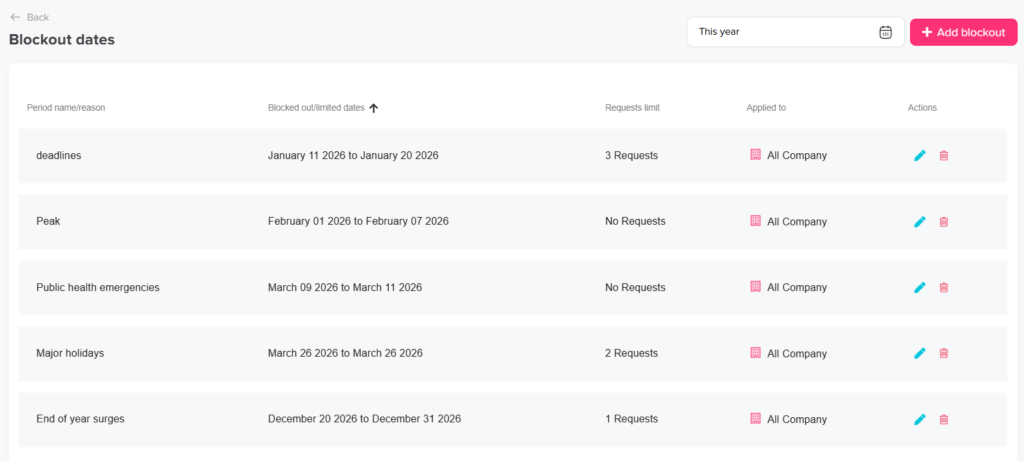
Use Structured Blackout Periods Strategically
Blackout periods are not about restricting employees they are about maintaining safe staffing during critical times.
Hospitals often experience predictable peak periods such as:
Major holidays
End of year surges
Public health emergencies
Accreditation or inspection periods
Instead of denying leave reactively, organizations should:
Define blackout periods annually
Communicate them early
Allow structured exceptions for emergencies
Track overrides for compliance purposes
When staff are informed in advance, they can plan accordingly, reducing frustration and perceived unfairness.
Digitize PTO Tracking and Approval Workflows
Manual PTO tracking using spreadsheets or email chains increases the risk of:
Double approvals
Miscalculated balances
Overlapping absences
Payroll discrepancies
Compliance issues
Healthcare organizations benefit significantly from digital PTO management systems that provide:
Real time leave balance visibility
Automated accrual calculations
Conflict detection alerts
Shift based deduction logic
Role based approval workflows
Full audit trails
Automation reduces administrative burden on HR teams and managers while increasing accuracy and transparency.
For multi location hospitals or clinic networks, centralized digital systems are essential to ensure consistency across branches.
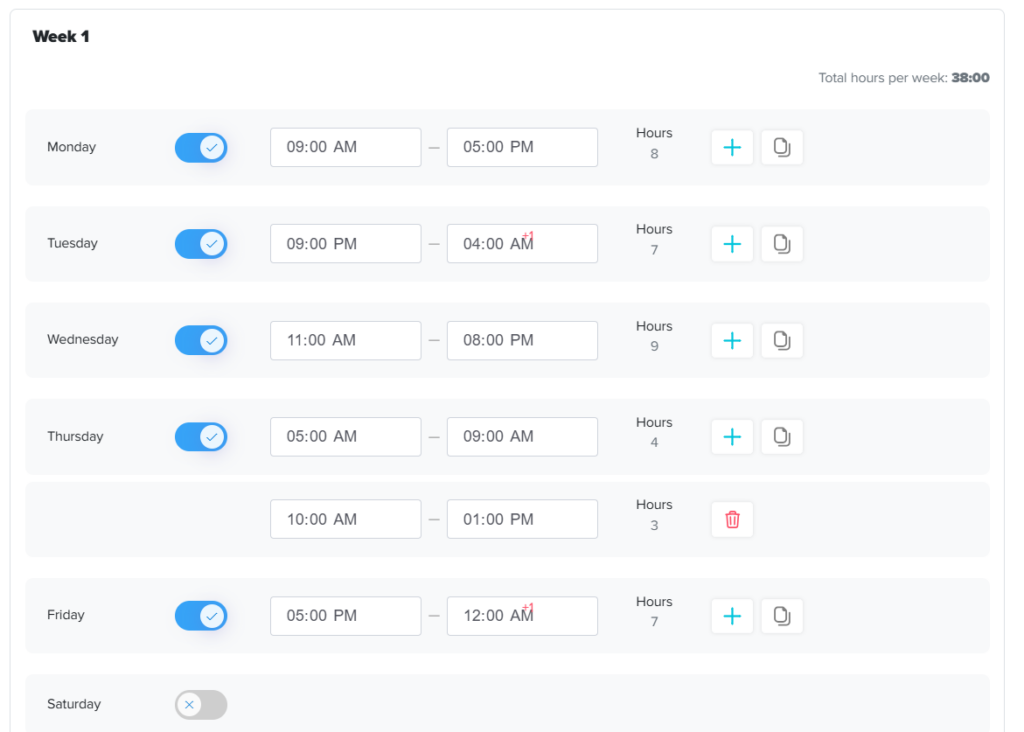
Work Schedule With Shift Based Scheduling
Healthcare staffing is shift driven, not calendar based.
PTO systems must accommodate:
8-hour, 10-hour, and 12-hour shifts
Overnight coverage
Rotating schedules
Flexible working hours
On call shifts
Split shifts
Calculating PTO in days can create inaccuracies for clinical staff. Instead, PTO should be managed in hours for greater precision.
For example:
A nurse working 12-hour shifts should have leave deducted accordingly.
Rotating schedules should automatically calculate hours based on assigned shifts.
Proper integration between PTO tracking and scheduling systems prevents staffing gaps and payroll errors.
Promote Fairness and Reduce Bias in Leave Approvals
Healthcare teams are tightly connected, and perceptions of favoritism can quickly damage morale.
To ensure fairness:
Apply standardized approval criteria
Track PTO distribution across the team
Rotate holiday priority annually
Avoid “first come, first served” models that disadvantage certain shift workers
Provide visibility into approval decisions
Data driven decision making protects managers from claims of bias and improves trust across teams.
Prepare for Emergency and Unplanned Leave
Unexpected absences are inevitable in healthcare.
A strong PTO management strategy includes contingency planning:
Cross training staff across units
Maintaining float pools
Establishing on call coverage rotations
Creating clear emergency reporting procedures
Enabling shift swap approvals within defined rules
Emergency leave should be documented clearly to maintain compliance while ensuring patient coverage remains intact.
Preparedness reduces panic-driven scheduling decisions.
Monitor PTO Usage to Prevent Burnout
Burnout is one of the most pressing challenges in healthcare today.
Ironically, some healthcare workers underutilize their PTO due to guilt, staffing shortages, or workload pressure.
Hospitals should monitor:
PTO utilization rates by department
Overtime frequency
Repeated last minute sick leave
Departments with unusually low leave usage
Encouraging regular time off supports:
Mental health
Clinical accuracy
Employee retention
Long term productivity
A workforce that rests consistently performs more safely and effectively.
Enable Multi Department and Multi Location Flexibility
Hospital networks often operate across multiple facilities and specialties.
Best practices include:
Location specific policies when required
Centralized reporting dashboards
Shared resource pools
Role based permissions for department managers
Consistent policy enforcement across sites
Central oversight with localized flexibility ensures operational control while allowing departments to adapt to their needs.
Ensure Compliance With Labor Laws and Healthcare Regulations
Healthcare organizations must comply with:
National and regional labor laws
Overtime regulations
Government mandated leave policies
Medical and family leave laws
Union agreements (if applicable)
PTO records must be:
Accurately calculated
Securely stored
Easily retrievable during audits
Consistently applied
Automation significantly reduces compliance risks and legal exposure.
Encourage Leadership Support for Time Off
Culture plays a significant role in PTO effectiveness.
If leadership subtly discourages leave, employees may avoid taking necessary breaks. This leads to fatigue, errors, and turnover.
Healthcare leadership should:
Model healthy leave usage
Avoid celebrating excessive overtime
Monitor staffing equity
Encourage open discussions about workload
Supporting PTO is not a weakness it is a patient safety strategy.
Conduct Annual PTO Strategy Reviews
Healthcare environments evolve due to regulatory changes, staffing challenges, and patient demand fluctuations.
Annual reviews should evaluate:
Staffing shortages linked to PTO
Overtime cost increases
Employee satisfaction surveys
Burnout indicators
Policy clarity and fairness
Continuous improvement ensures PTO policies remain aligned with operational realities.
FAQ
Why is PTO management more complex in hospitals and clinics?
Healthcare facilities operate 24/7 and must maintain strict staffing ratios to ensure patient safety. Unlike office environments where tasks can sometimes be delayed or redistributed, clinical roles require qualified coverage at all times. PTO decisions directly affect patient care, regulatory compliance, and overtime costs, making structured planning essential.
How far in advance should healthcare staff request PTO?
Best practice is to require advance notice for planned leave typically two to four weeks for standard vacation and longer notice for extended leave. Sick or emergency leave should be reported immediately according to hospital protocol. Advance planning allows managers to evaluate staffing coverage and avoid last minute disruptions.
Should hospitals limit how many employees can take PTO at the same time?
Yes. Most healthcare organizations set department level or shift level caps. For example, only a certain number of nurses per unit may be approved for leave during the same shift. This prevents understaffing while maintaining fairness across the team.
How can hospitals handle PTO during peak seasons like flu season?
Hospitals should identify peak periods in advance using historical data, establish structured blackout periods, stagger leave approvals, and maintain float pools or cross trained backup staff. Proactive planning minimizes operational risk during high demand seasons.
Is it better to track PTO in days or hours for healthcare staff?
For clinical environments, tracking PTO in hours is more accurate. Healthcare professionals often work 12-hour shifts, rotating schedules, overnight shifts, or split shifts. Hourly tracking ensures correct deductions and avoids payroll discrepancies.
How can PTO management reduce burnout in healthcare workers?
Monitoring PTO usage helps identify employees who rarely take leave. Encouraging regular time off improves mental health, reduces fatigue related errors, increases retention, and enhances overall patient care quality. A structured PTO system supports long term workforce sustainability.
What happens if multiple critical staff request the same dates off?
Managers should evaluate requests based on staffing coverage requirements, approval history, fair rotation policies, and operational impact. Having predefined approval rules prevents favoritism and ensures transparency in decision making.
How should hospitals manage emergency or last minute leave?
Best practices include maintaining an internal float pool, allowing structured shift swaps, cross training staff, and using automated scheduling tools to quickly identify coverage gaps. Prepared contingency plans reduce stress and operational disruption.
Can PTO policies differ between departments or locations?
Yes. Multi location hospitals or clinics may apply location specific policies based on patient demand, local labor laws, staffing availability, and operational needs. However, core policy principles should remain consistent across the organization to ensure fairness.
How does digital PTO software improve healthcare operations?
Digital systems provide real time leave balance visibility, automated accrual calculations, conflict detection before approval, audit trails for compliance, and integration with shift scheduling. This reduces administrative burden, prevents errors, and protects staffing stability.
How often should PTO policies be reviewed?
Healthcare organizations should review PTO policies at least annually, or sooner if staffing shortages increase, overtime costs rise, employee satisfaction declines, or regulations change. Regular reviews ensure policies remain practical and aligned with operational realities.
Does encouraging PTO really improve patient care?
Yes. Well rested healthcare professionals are more attentive, less prone to clinical errors, more engaged with patients, and less likely to leave the organization. Supporting time off is not just an employee benefit it is a patient safety strategy.
Conclusion
Effective PTO management in hospitals and clinics is a balancing act between employee wellbeing and patient safety.
When implemented strategically, it:
Protects staffing stability
Reduces burnout
Controls overtime costs
Enhances fairness
Supports compliance
Improves patient outcomes
Healthcare organizations that treat PTO management as a strategic workforce function not just an HR process create more resilient, satisfied, and high performing teams.

