In the dynamic world of Human Resources (HR), effectively managing employee time-off is crucial for maintaining a productive, happy workforce. This is where Day Off Leave Tracker comes into play, offering a streamlined, efficient solution for tracking employee absences. Let’s delve into how this tool can be a game-changer for HR professionals.
The Importance of Efficient Leave Management
Before examining the specifics of a leave tracker, it’s important to understand why efficient leave management is vital. It ensures compliance with labor laws, helps maintain adequate staffing levels, and supports a healthy work-life balance for employees. Mismanagement, on the other hand, can lead to staffing shortages, legal issues, and decreased employee morale.
What is Day Off Leave Tracker?
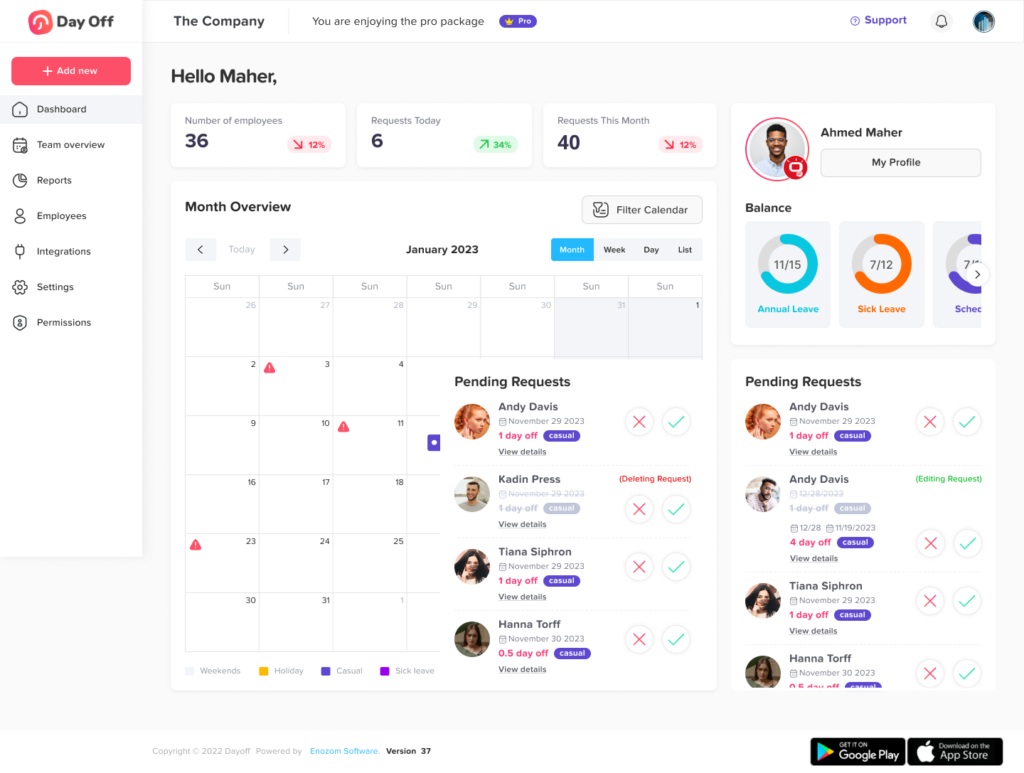
Day Off Leave Tracker centralizes every kind of absence, vacations, PTO, sick days, and personal leave into one intuitive workspace. HR, managers, and employees share a single source of truth for policies, balances, requests, and approvals, replacing scattered spreadsheets and email threads with a clean, real-time system.
Core Capabilities
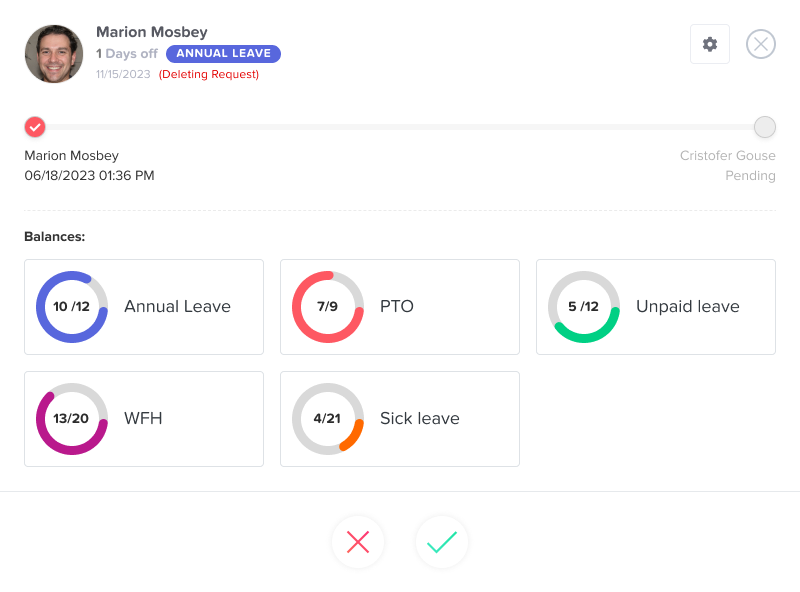
At its heart, Day Off provides accurate tracking of leave balances and usage across multiple leave types. Organizations can run different policies for different groups, by country, department, seniority, or contract type, without losing consistency. Employees always see their up-to-date balances and history, while HR gets a complete view of who’s off, when, and why.
Custom Approval Workflows
No two teams approve leave the same way. Day Off lets you mirror your real workflow, whether that’s a simple manager sign-off or a multi-step path through team leads, HR, and payroll. Approvals can be delegated when approvers are away, and escalations ensure requests never stall. The result is a fast, transparent process with clear accountability.
Seamless Integrations
Approved time off should instantly reflect where work is planned. Day Off connects to Google Calendar and Outlook so absences appear on shared calendars the moment they’re approved. Native Slack updates keep everyone informed without switching tools. Importing employees is straightforward, and SSO support makes onboarding effortless for IT and HR.
Accruals and Compliance
Accrual rules can match your policy precisely, monthly or biweekly accruals, proration for joiners and leavers, carryover caps, and optional cash-out. Regional holidays and localized rules are supported, helping global teams stay compliant. Every action is recorded with timestamps to create a reliable audit trail for HR and legal reviews.
Planning and Coverage
Approving time off is easier when you can see the big picture. Day Off highlights overlaps and capacity risks before you click “approve,” helping managers maintain minimum staffing levels and schedule backups for key roles. This proactive view prevents bottlenecks, protects service levels, and reduces last-minute firefighting.
Employee and Manager Experience
Employees can request or cancel leave in seconds from web or mobile, with clear guidance on policy and real-time balance updates. Managers get a focused dashboard that surfaces conflicts, suggests alternatives, and makes approvals quick but thoughtful. The tone throughout the app is friendly and direct, encouraging healthy time-off habits.
Insights and Reporting
Dashboards reveal patterns that matter: peak absence periods, teams with low PTO usage (a burnout red flag), projected carryover liabilities, and payroll-ready summaries. HR can export the exact files finance needs for accruals and close, and track how policy changes affect utilization over time.
Security and Reliability
Role-based permissions keep sensitive data accessible only to the right people. Encryption, uptime commitments, and regular backups protect operations, while regional hosting options support data residency needs. You can trust the system to be available when planning and approvals are most critical.
Tangible Benefits
Day Off reduces administrative workload, shortens approval cycles, and brings transparency to a process employees care deeply about. It improves coverage planning, strengthens compliance, and promotes a positive vacation culture, one where time off is encouraged, predictable, and genuinely restorative.
Getting Started
Set up policies, define approval flows, connect calendars and Slack, and import your people. From there, employees submit requests, managers approve with context, and HR monitors trends and exports reports. Most teams go from setup to confident usage in a single afternoon.
Best-Practice Tips
Publish a one-page leave guide in plain language and link it inside the app. Train managers to plan coverage and model healthy PTO use. Review policies quarterly to fine-tune accruals, carryover caps, and blackout dates. Most importantly, communicate that time off is meant to be used, then make it easy to do so.
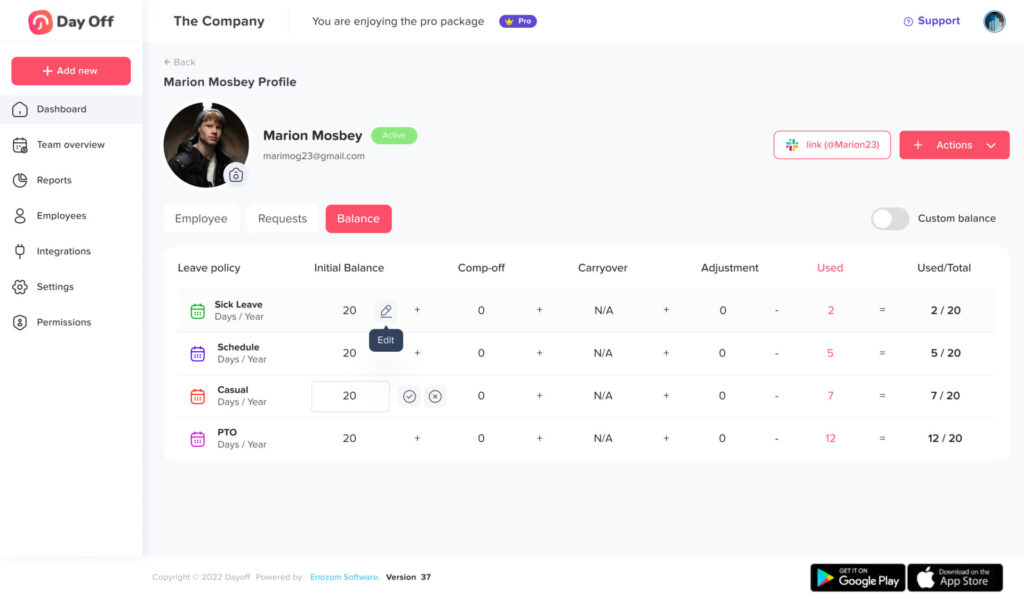
Automated Notifications
Automated notifications ensure the right people get the right information at the right moment. When an employee submits a request, the assigned approver is alerted instantly; once a decision is made, the requester and any impacted stakeholders (project leads, schedulers) are notified without HR chasing emails. Beyond requests and approvals, announcements like policy updates, upcoming blackout periods, and holiday calendars can be broadcast in advance to reduce last-minute surprises.
Notifications can be delivered where teams already work, email, in-app, and channels like Slack or Teams, and can be configured by role and urgency. Approvers might receive real-time pings, while employees get a daily digest. Quiet hours and time-zone awareness prevent overnight interruptions, and an audit log records who was notified and when for compliance. The net effect is fewer bottlenecks, faster cycle times, and a shared, up-to-date picture of who’s off and what’s changing.
Sub-Teams Creation
Large organizations rarely operate on a single set of rules. Sub-teams allow HR to mirror real structures, departments, regions, shifts, each with its own policies, balances, working days, and holidays. A sales sub-team might accrue PTO monthly with weekend coverage, while an engineering sub-team follows a different accrual rate and a four-day workweek. Policies can inherit from a parent team and override only what’s different, keeping administration clean while respecting local nuances.
Sub-teams also improve operations. Approval workflows can route differently by team (e.g., store manager, area HR for retail, squad lead, HRBP for tech). Availability views roll up from sub-teams to the parent, so managers see both local coverage and organization-wide capacity before approving requests. Reporting benefits too: HR can compare utilization, carryover risk, and burnout signals across sub-teams, then tune policies where they’ll have the most impact.
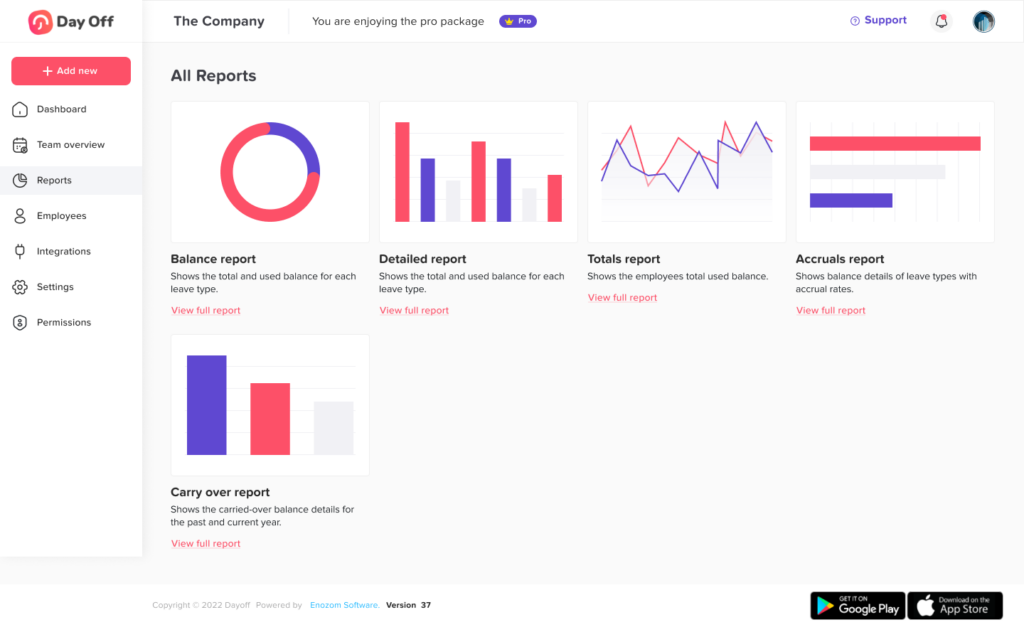
Powerful Reporting Tools
Day Off’s reporting tools give HR and leadership teams a clear, data-driven understanding of how employees use their time off. Instead of relying on scattered spreadsheets or manual calculations, the system generates comprehensive reports that detail leave balances, accrual trends, usage rates, and upcoming absences. These insights empower HR professionals to identify patterns, such as teams at risk of burnout, departments with low PTO utilization, or peak vacation seasons that require extra coverage.
Reports can be filtered by department, location, employment type, or time frame, making it easy to tailor insights to specific business needs. They also integrate seamlessly with finance and payroll functions, helping forecast future liabilities and simplifying month-end reconciliations. Beyond compliance and recordkeeping, this visibility supports strategic workforce planning, ensuring the right staffing levels year-round and promoting a healthier, more balanced workplace.
Mobile Accessibility
In today’s hybrid and fast-moving work environment, accessibility is non-negotiable. Day Off’s mobile app brings the full power of leave management to the palm of your hand. Employees can submit vacation or sick leave requests, check remaining balances, and receive approval notifications instantly, no need to log into a desktop system.
Managers can review and approve requests on the go, view team calendars, and manage conflicts directly from their smartphones, ensuring that decisions are made quickly and transparently. Push notifications keep everyone aligned in real time, while the intuitive interface makes it easy to navigate even for non-technical users.
This mobile-first approach enhances convenience, efficiency, and responsiveness, ensuring that leave management keeps pace with modern work habits. Whether in the office, on-site, or remote, Day Off ensures that managing PTO and absences is always just a tap away.
Security and Data Protection
Day Off places a strong emphasis on data security and privacy. The platform uses data encryption both during transmission and at rest. It operates on secured data centers with certifications like AICPA, SOC 2 Type II, and SOC 3 Type II. Additionally, the app ensures daily data backups and robust disaster recovery protocols to protect user data.
User Experiences
The application has garnered positive feedback from various users, including HR professionals and managers. Users have praised its ease of setup and implementation, its integration with existing systems like Google Calendar. And the clarity it brings to managing leaves and PTO. The shared calendar feature and user-friendly interface are particularly appreciated. As they contribute to a more organized and transparent leave management process.
Plans and Availability
Day Off Vacation Tracker offers a free version, allowing unlimited employees to be tracked, which is suitable for businesses of all sizes. For more advanced features, there is a PRO version available, offering additional functionalities for comprehensive leave management.
FAQ: Transitioning to a Digital Leave Tracker
How difficult is it to move from a manual to a digital leave system?
Transitioning is typically straightforward with modern, user-friendly platforms like Day Off. Guided onboarding, templates, and in-app tips help you configure policies, import employees, and set approval flows quickly. Success hinges on clear communication and brief training for managers and employees so everyone knows what’s changing and why.
Will a digital leave tracker integrate with our existing HR tools?
Most leading systems, including Day Off, offer integrations or APIs for common HRIS, payroll, and communication tools. Confirm available connectors (e.g., Google/Outlook calendars, Slack) and any data fields you need synced (employees, balances, cost centers) to ensure a smooth two-way flow.
Is our data secure with a digital leave solution?
Reputable providers prioritize security with encryption in transit and at rest, role-based access controls, audit logs, and regular backups. Ask for details on data residency, compliance standards (e.g., SOC 2, ISO 27001), and incident response processes to match your organization’s risk posture.
How does the system handle different leave policies and rules?
Digital trackers are highly configurable. You can set multiple leave types, accrual rates, proration for joiners/leavers, carryover caps, cash-out rules, blackout dates, and team-specific calendars. This flexibility supports diverse workforces across departments, regions, and employment types.
What is the cost impact of going digital?
Pricing varies by features and headcount, but most platforms offer tiered plans that scale with your needs. Consider total ROI: reduced admin time, fewer errors, faster approvals, better coverage planning, and improved compliance typically offset subscription costs.
How do we drive employee adoption?
Start with a clear “what/why/when” announcement, offer short role-based training (employees vs. managers), and provide quick-start guides. Enable single sign-on for easy access, and gather early feedback to refine policies or workflows. Manager buy-in is critical, when leaders use it, teams follow.
Can the system support complex accrual calculations?
Yes. Advanced accrual engines handle monthly/biweekly accruals, tenure-based tiers, negative balances, minimum/maximum accrual limits, and regional holidays. Scenario testing in a sandbox helps validate rules before go-live.
What support is available if we need help?
Choose a provider with responsive support: knowledge base, video tutorials, in-app chat or ticketing, and dedicated success resources for onboarding. Clarify SLAs and escalation paths, especially around payroll cutoffs and peak vacation seasons.
How does a digital tracker improve leave management versus manual methods?
Automation eliminates spreadsheet errors and email back-and-forth. You gain real-time balances, conflict alerts, approval workflows, calendar sync, and reporting for finance and HR. The result is faster cycle times, better staffing decisions, and a more transparent employee experience.
Can the system be branded to match our company identity?
Many platforms allow light branding, logo, colors, subdomain, and customizable policy text and notifications. This creates a familiar, trustworthy experience that aligns with your internal tools and culture.
Conclusion
Employees leave tracker is more than just a convenience; it’s a strategic tool that can significantly improve the efficiency of leave management. By automating processes, ensuring compliance, and providing valuable insights, it supports a more organized, fair, and transparent approach to handling employee time off. As such, it’s an invaluable asset for any HR department looking to streamline its operations and foster a positive workplace culture.
Day Off is a robust and secure leave management tool that caters to the diverse needs of modern organizations. Its combination of user-friendly features, strong security protocols, and positive user feedback makes it an excellent choice for businesses seeking an efficient and reliable solution for managing employee leaves and PTO.