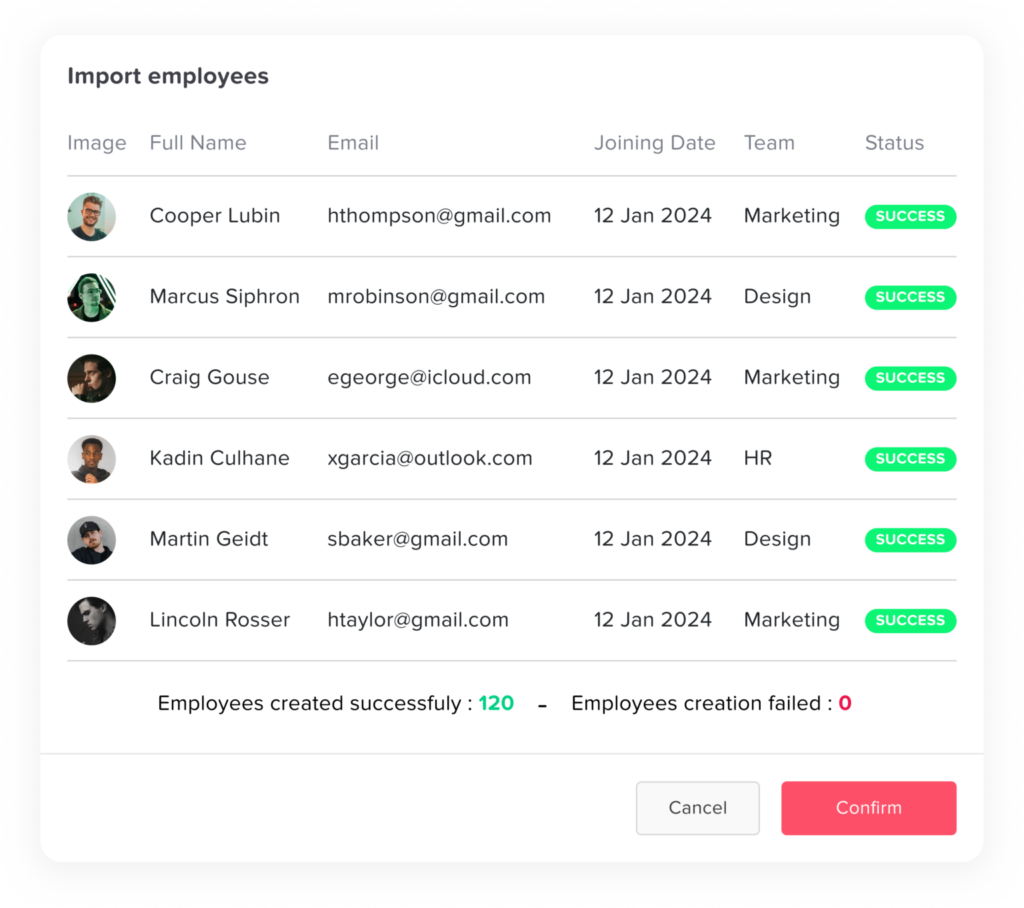
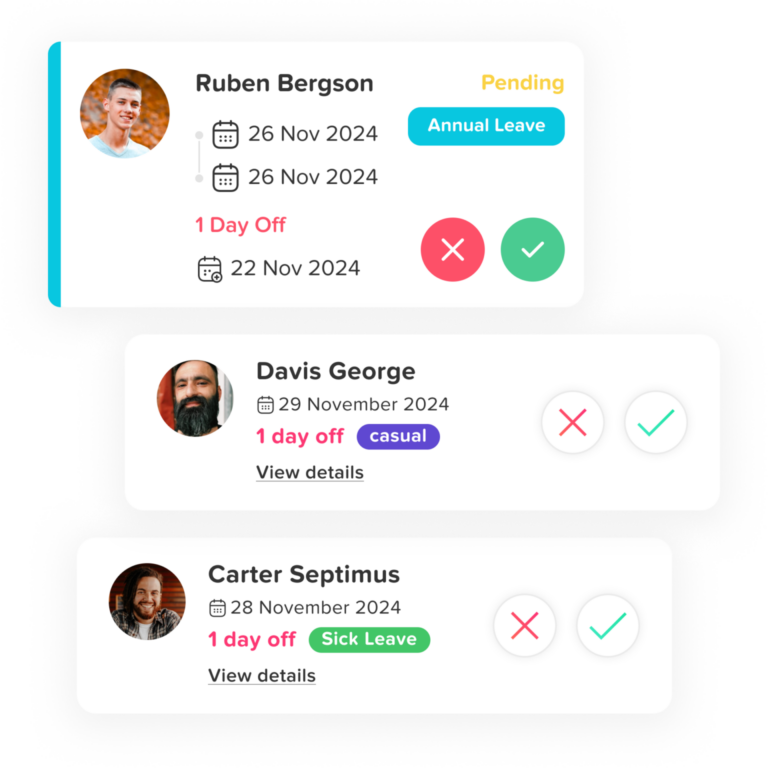
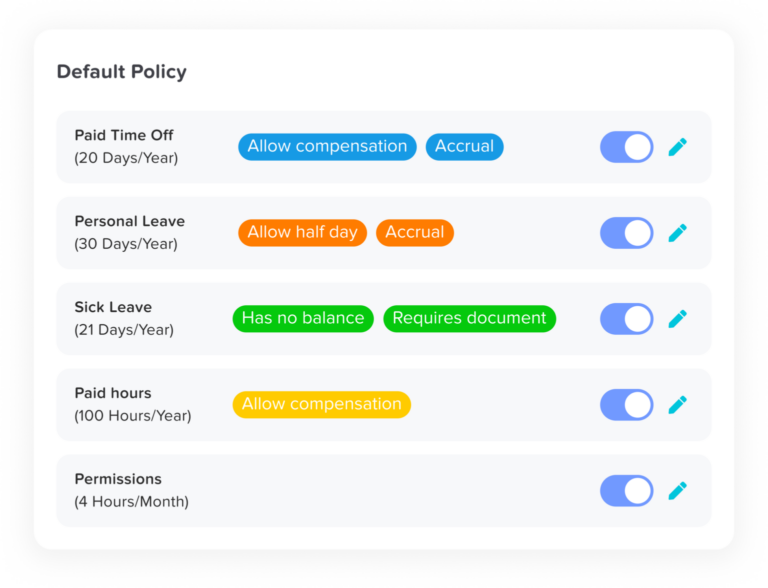
A leave management app is a digital tool that helps organizations handle employee time off easily and efficiently. Instead of using paper forms, spreadsheets, or long email threads, everything is managed in one simple, automated system. The app keeps track of all types of leave, like vacation days, sick leave, parental leave, or unpaid time off, and makes sure company policies are applied fairly. With this kind of app, HR teams and managers can save time, avoid mistakes, and keep everything clear and organized for everyone.
Why Your Organization Needs a Leave Management App
Without a dedicated tool, managing employee leave can quickly become chaotic and error-prone. A leave management app brings structure and control, reducing the chances of scheduling conflicts, payroll discrepancies, or policy misunderstandings. It ensures employees know their leave entitlements and history, while management gains instant insight into availability, trends, and compliance risks. Such automation saves countless hours in HR processing, boosts team morale through transparency, and provides vital data for decision-making. In industries where staffing levels must remain optimal, this kind of system is not just helpful, it’s essential.
Day Off: A Comprehensive Leave Management App
Day Off is a feature-rich leave management solution tailored to the modern workplace. Whether you’re a small startup or a large enterprise with multiple departments and global teams, Day Off App delivers powerful yet user-friendly tools to simplify time-off tracking. It stands out for its intuitive interface, mobile-first design, and robust policy flexibility. With clients ranging from global franchises like McDonald’s to nimble tech firms, Day Off proves that even the most complex leave policies can be managed with ease and efficiency.
Flexible Leave Policy Engine
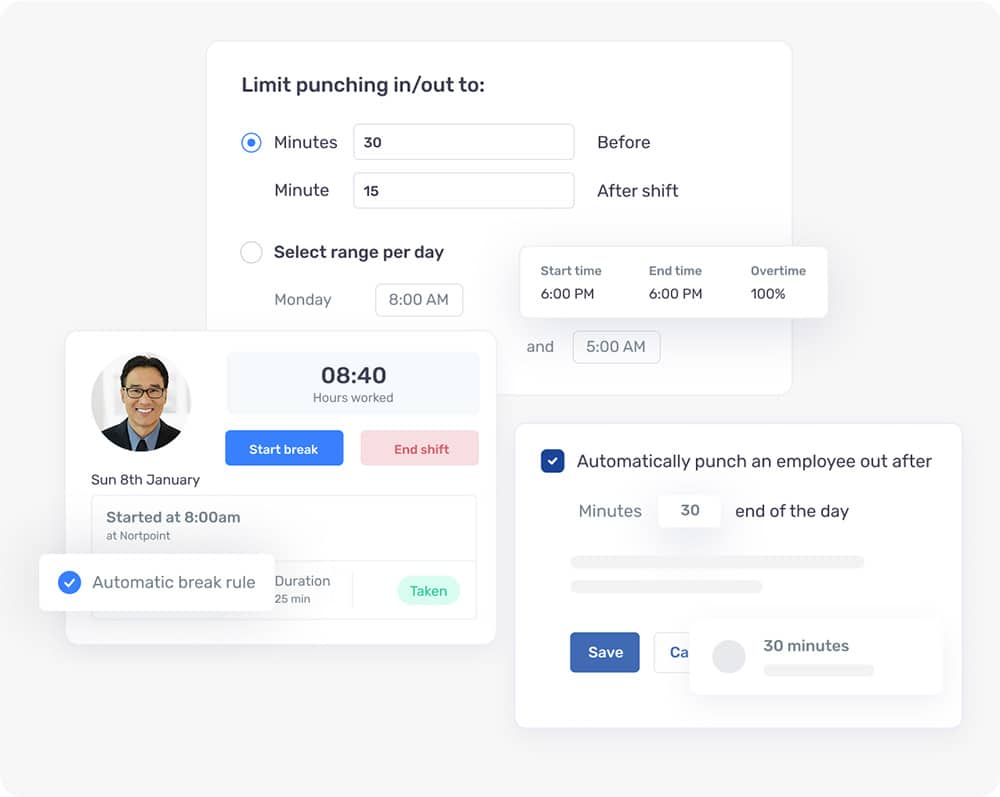
Day Off empowers organizations to create and enforce leave policies that match their exact needs. You can define different types of leave, such as annual vacation, sick leave, maternity/paternity, bereavement, and compensatory time, and set unique rules for each. Whether your policy involves monthly accruals, annual grants, or milestone-based entitlements, the platform can accommodate it. You can also specify carryover limits, enforce expiry dates, and allow or restrict negative balances to align with your operational or legal requirements.
Automated Requests and Approvals
Gone are the days of chasing down signatures or sifting through email threads. With Day Off, employees submit leave requests directly through the app or website. These requests are automatically routed to the appropriate approvers based on your organizational structure. Managers can review and respond in seconds, while the system sends notifications at every step. For HR, this means fewer delays and greater consistency. For teams, it means clarity and quicker decisions.
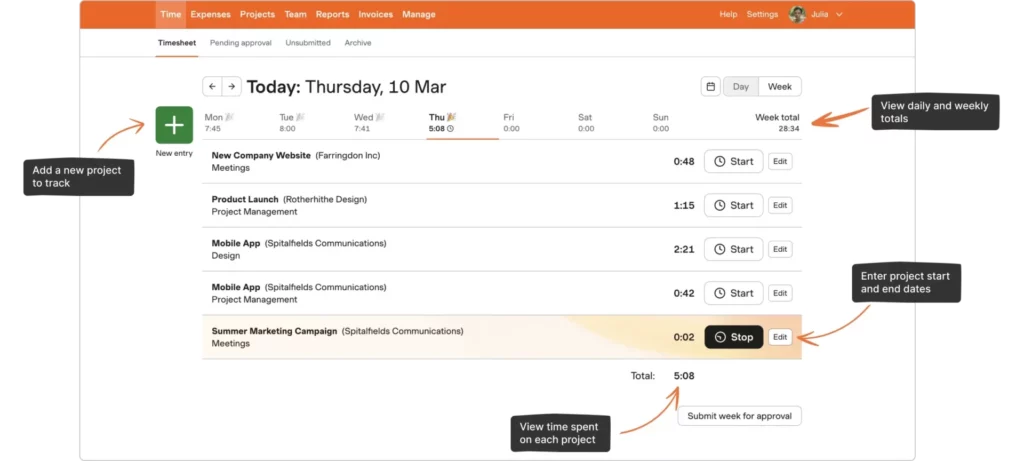
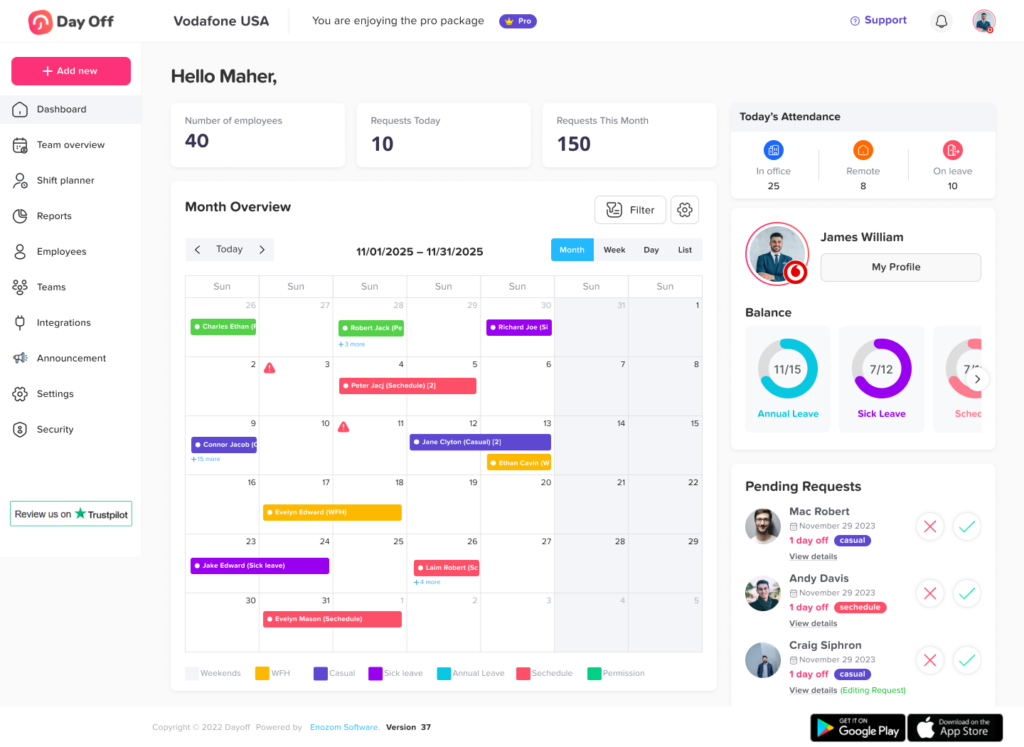
Real-Time Balances and Transparency
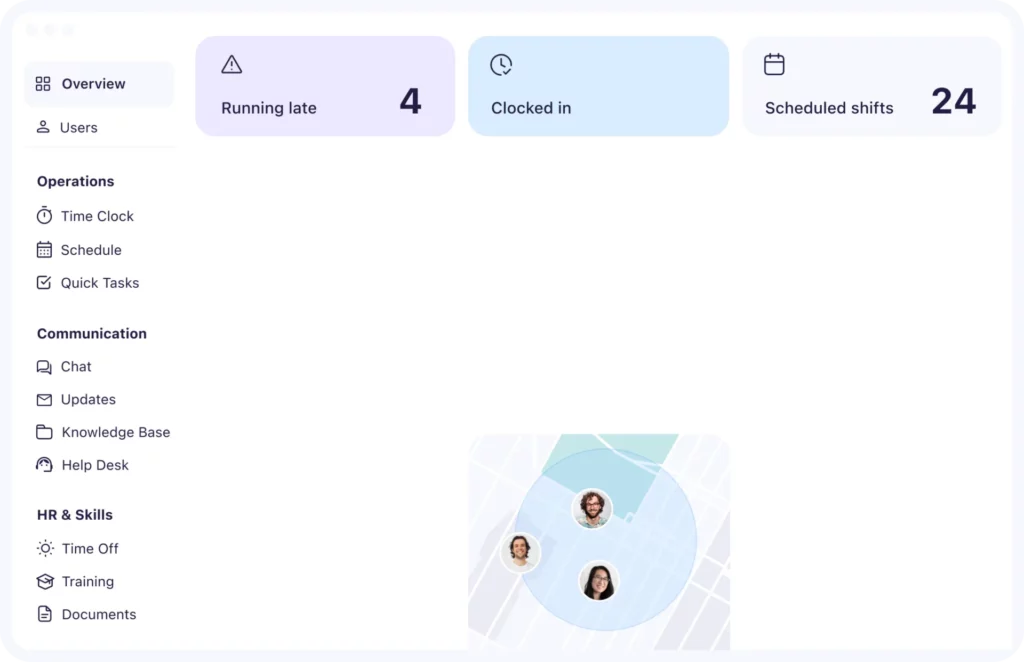
Day Off keeps everyone informed by displaying real-time leave balances and request histories. Employees can log in at any time to see how many days they have left, how much they’ve used, and whether any pending requests are awaiting approval. Managers can view leave schedules across their teams, ensuring they maintain adequate coverage at all times. This transparency reduces misunderstandings and empowers both employees and leadership with up-to-date information.
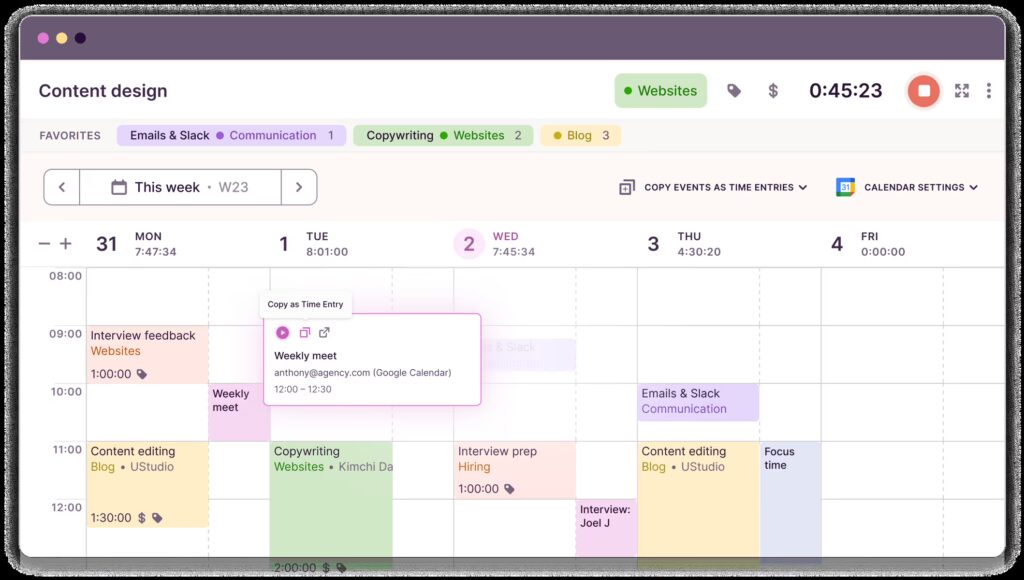
Calendar Integration and Team Visibility
The app offers seamless integration with tools like Google Calendar, Outlook, Slack, and Microsoft Teams. This allows approved leaves to automatically appear in shared calendars, helping teams plan around upcoming absences. Additionally, a team-wide view of who’s in and out of the office helps avoid bottlenecks and overlap, especially during critical business periods or project deadlines.
Mobile-First Accessibility
With a sleek mobile app for both iOS and Android, Day Off is built for today’s on-the-go workforce. Employees can submit requests, check their balance, and receive approval notifications from anywhere. Managers can quickly approve or deny requests even while away from their desks. This mobility ensures that the leave management process doesn’t stall just because someone isn’t at their computer.
Powerful Reporting and Analytics
Day Off includes built-in dashboards and exportable reports that provide deep insights into leave usage patterns. HR teams can analyze leave trends across departments, identify seasonal peaks in absenteeism, and monitor compliance with company policies or labor regulations. These analytics are crucial for strategic workforce planning and can help prevent burnout or overstaffing.
Why Choose Day Off Over Other Leave Management Apps?
Quick Setup
With Day Off, you can have your leave management system up and running in just a few minutes. You start by creating your company account, adding your basic info, and then inviting team members, either one-by-one or via bulk import. After that you set up working days, leave types, and locations if needed. This means no long waiting time or complex onboarding, just clear setup and you’re ready to go.
User-Friendly Design
Day Off is built so that both managers and employees can use it easily, with almost no training required. The interface is modern, intuitive and self-explanatory. For employees, for example, you can check your leave balance and submit a request in just a few clicks. Managers get a clear view of all pending requests, history, and team availability. The simplicity helps reduce mistakes and makes adoption across the team smoother.
Full Mobile Access
Whether you’re at your desk or on the go, Day Off has you covered. It offers full mobile access so employees can submit leave requests, check balances, and view their status from their mobile device. Managers can approve or reject requests and stay updated no matter where they are. This is especially helpful for remote teams or employees who travel frequently.
Advanced Customization
Not all companies are the same, and Day Off understands that. You can build complex leave structures, including: multiple leave policies for different teams or locations; leave accruals (for example, earning leave over time); carry-over rules for unused leave; and even negative balances or half-day options. You can assign policies to whole locations, specific teams, or even individual employees. This flexibility means the tool can adapt to your real business needs rather than forcing you to adapt to it.
Seamless Integrations
Day Off connects with the tools you already use. For example, it integrates with Google Calendar, Outlook Calendar, Slack, and Microsoft Teams so that approved time off automatically shows up in calendars and relevant communication channels. This helps keep everyone aligned and avoids scheduling clashes, no more manual syncing or missed updates.
Day Off Pricing & Plans
Startup
- 25 Employees
- Single Approver
- Three Policies
- Unlimited Team
- Unlimited Locations
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can I try the Pro plan before subscribing?
Yes! Day Off offers a 14-day free trial of the Pro plan, giving you full access to every premium feature with no credit card required. During the trial, you can explore advanced leave policies, automated accruals, approval workflows, integrations with tools like Slack and Outlook, and more. This lets you experience how the app fits into your daily HR operations before making a purchase decision. At the end of the trial, you can easily upgrade to continue using Pro features, or stay on the free plan if it meets your needs.
Is Day Off suitable for global teams?
Absolutely. Day Off is designed for companies that operate across multiple countries, time zones, and office locations. You can manage teams in different regions from one centralized dashboard, with local time and holiday calendars applied automatically. The app supports multiple languages and currencies, ensuring a smooth experience for all team members no matter where they work. For global HR managers, this means consistent leave tracking and fewer communication errors across borders.
How secure is our employee data in Day Off?
Security is a top priority for Day Off. The platform uses industry-standard SSL encryption to protect your data during transmission and securely stores it on trusted cloud infrastructure. Access is role-based, meaning only authorized personnel, like HR admins or managers, can view or manage employee leave data. In addition, Day Off follows modern data protection standards and regular security audits to keep your company’s sensitive information safe and compliant with international privacy laws such as GDPR.
Can we customize leave types and rules?
Yes, customization is one of the biggest strengths of Day Off. You can create unlimited custom leave types, from standard vacation days and sick leave to special types like volunteer days or study leave. Each leave type can have its own accrual rate, carryover limits, and approval rules. The system also supports multi-level approval workflows, letting you design a process that matches your company’s internal HR policies. This flexibility makes it easy to adapt Day Off to organizations of any size or structure.
Does Day Off support different holiday calendars?
Yes. Day Off lets you import official public holidays for specific countries or regions with just a few clicks. You can also edit or add your own company holidays, such as internal events or office shutdown periods. This ensures that leave balances and availability reflect the correct working days for each location. For global companies with teams in multiple countries, it’s a convenient way to manage region-specific calendars without manual tracking or confusion.
Is it possible to block time-off during key periods?
Definitely. With Day Off, admins can define blackout periods, specific dates when leave requests are temporarily restricted. This is ideal for crucial business times like product launches, financial closing periods, or peak seasons when all hands are needed on deck. Employees will automatically be notified if they attempt to request time off during these blocked periods. This feature helps organizations maintain productivity and ensures that critical projects stay on schedule.
Can employees request hourly or partial-day leave?
Yes, the Pro plan includes advanced flexibility for time-off tracking. Employees can request leave by the hour or for half-days instead of taking a full day off. This is especially useful for teams with shift work, flexible schedules, or employees who need short breaks for appointments or personal matters. Managers can view these partial requests clearly within the dashboard and approve them just like any other leave type, keeping the process consistent and transparent.
How does Day Off integrate with other tools?
Day Off integrates seamlessly with the tools your team already uses. You can connect it with Google Calendar, Outlook, Slack, and Microsoft Teams to automatically sync approved time-off events and keep everyone informed. For example, when someone’s vacation is approved, it appears instantly on shared calendars or within your Slack workspace. These integrations help reduce scheduling conflicts, improve visibility across departments, and make sure your team always knows who’s available.
What happens if we go over 10 users on the Free plan?
Once your team grows beyond 10 users, Day Off will prompt you to upgrade to the Pro plan. The Pro plan supports unlimited users, making it ideal for growing businesses or larger organizations. Upgrading also unlocks powerful features like multi-layer approvals, advanced analytics, and automated accruals. This ensures that as your company scales, your leave management system continues to operate smoothly without limitations or manual workarounds.
Conclusion
Using a leave management app has become essential rather than optional. A tool like Day Off simplifies every part of managing time off, from setting policies and approving requests to tracking trends and reports. Whether you’re leading a small startup or overseeing a global team, Day Off gives you the flexibility, clarity, and automation you need to manage leave smoothly and fairly. By replacing old manual methods with a digital system, your organization saves time, reduces errors, and builds a more organized, transparent workplace where teams can plan confidently and stay compliant.