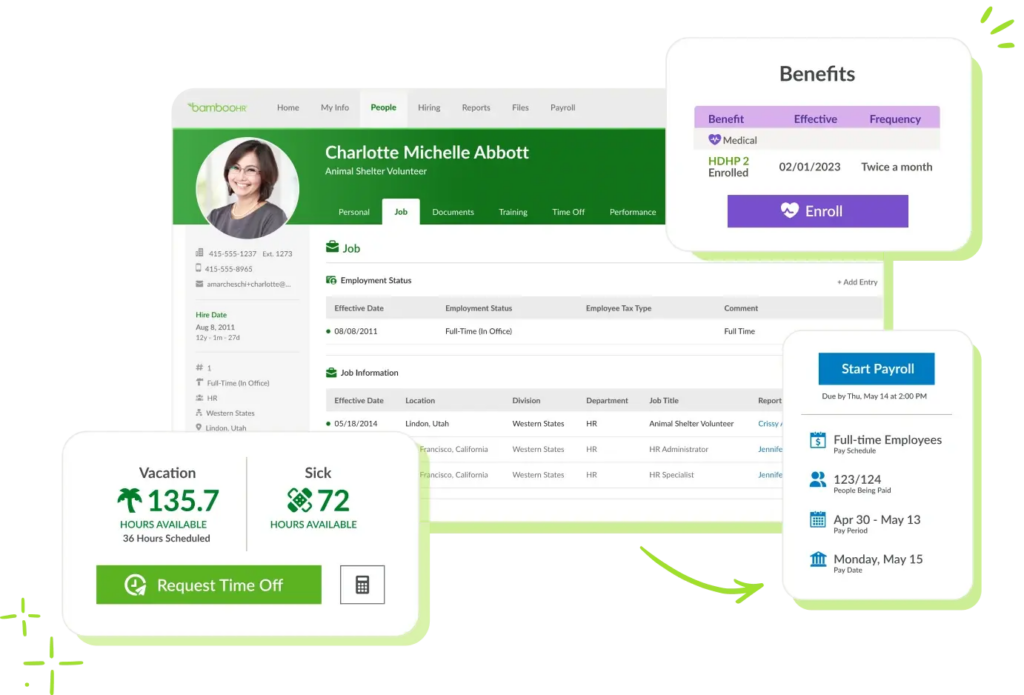
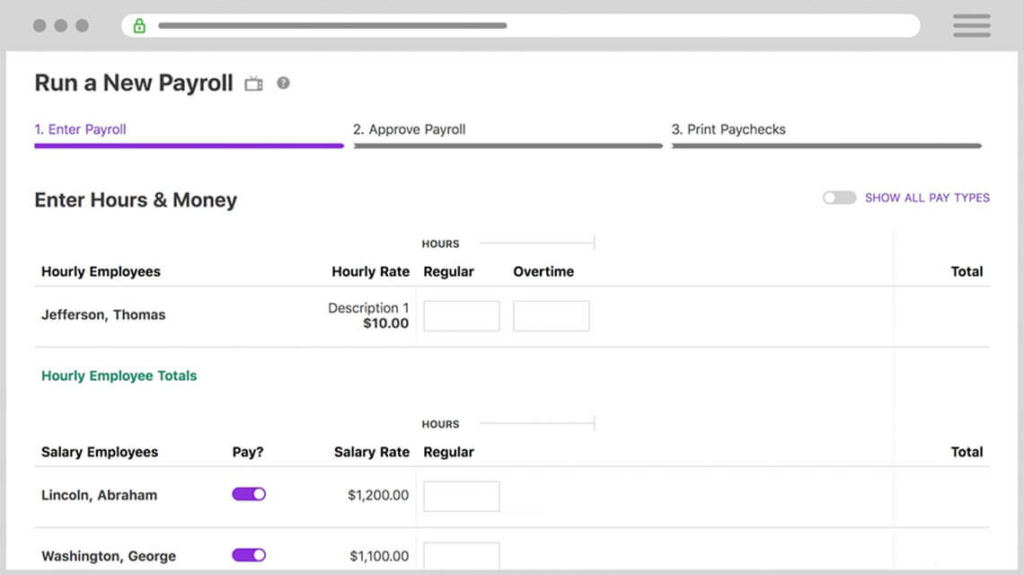
The topic of employee benefits has become increasingly prominent, with a particular focus on Leave Management and the entitlements of part-time employees. Historically, those in full-time positions have enjoyed access to a wider array of benefits, such as paid time off (PTO), health insurance, and retirement plans. However, the shift towards more flexible employment models, including part-time and gig work, has prompted businesses to rethink and redesign their benefits packages.
This is being done in an effort to attract and maintain a diverse pool of talent by accommodating the varying needs of employees across different work statuses. In this detailed exploration, we will dive deep into the benefits landscape for part-time workers, with a special emphasis on PTO. We aim to uncover how contemporary companies are modifying their benefits strategies to align with the changing dynamics of the workforce, ensuring they meet the expectations and requirements of a varied and evolving employee base.
Understanding Part-Time Employment
Part-time employment is typically defined by the number of hours an employee works, which is usually less than a full-time schedule. While definitions can vary, The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), which sets standards for wages and hours, does not specify the hours that differentiate full-time and part-time employment. This classification is often determined by the employer.
Are Part-Time Employees Eligible for PTO?
The short answer is: it depends. There is no federal mandate requiring employers to provide paid time off to any employees, full-time or part-time. However, many employers choose to offer PTO as a benefit to attract and retain talent. The eligibility and amount of PTO provided to part-time employees can vary significantly from one company to another. Some businesses may offer prorated PTO based on the number of hours worked, while others may have specific policies that part-time employees must meet to qualify for PTO.
Examples of Part-Time Employee PTO Policies:
-
- Prorated PTO: A company might offer PTO to part-time employees on a prorated basis. For example, if a full-time employee receives 10 days of PTO annually, a part-time employee working half the hours might be eligible for 5 days.
-
- Accrual System: Some organizations use an accrual system where employees earn PTO hours based on the number of hours worked. This system can be particularly beneficial for part-time employees as it directly ties PTO accumulation to hours on the job.
Other Benefits for Part-Time Employees
Besides PTO, part-time employees may be eligible for other benefits. These can include:
-
- Health Insurance: The Affordable Care Act (ACA) requires employers with 50 or more full-time employees to offer health insurance to those working at least 30 hours per week, which can include part-time workers.
-
- Retirement Plans: Employers may extend eligibility for retirement benefits, such as a 401(k), to part-time employees, often after meeting certain criteria like working a minimum number of hours or completing a year of service.
-
- Dental and Vision Insurance: Some companies offer dental and vision insurance to part-time employees, which can be a significant perk.
-
- Employee Discounts and Perks: Discounts on products and services, flexible schedules, and access to training programs are common benefits that can be extended to part-time staff.
Best Practices for Employers
To effectively manage and offer benefits to part-time employees, employers should consider the following best practices:
-
- Clear Communication: Clearly communicate the criteria and details of benefits eligibility to all employees. Transparency helps in setting the right expectations and fosters a positive work environment.
-
- Equity and Inclusion: Strive for policies that are inclusive and equitable. Consider the needs and preferences of part-time employees when designing benefits packages.
-
- Flexibility: Be open to feedback and willing to adjust policies as needed. The workforce and its needs are constantly evolving, requiring employers to be adaptable.
The Role of Technology in Managing Part-Time Benefits
Simplifying Part-Time Benefits with Day Off
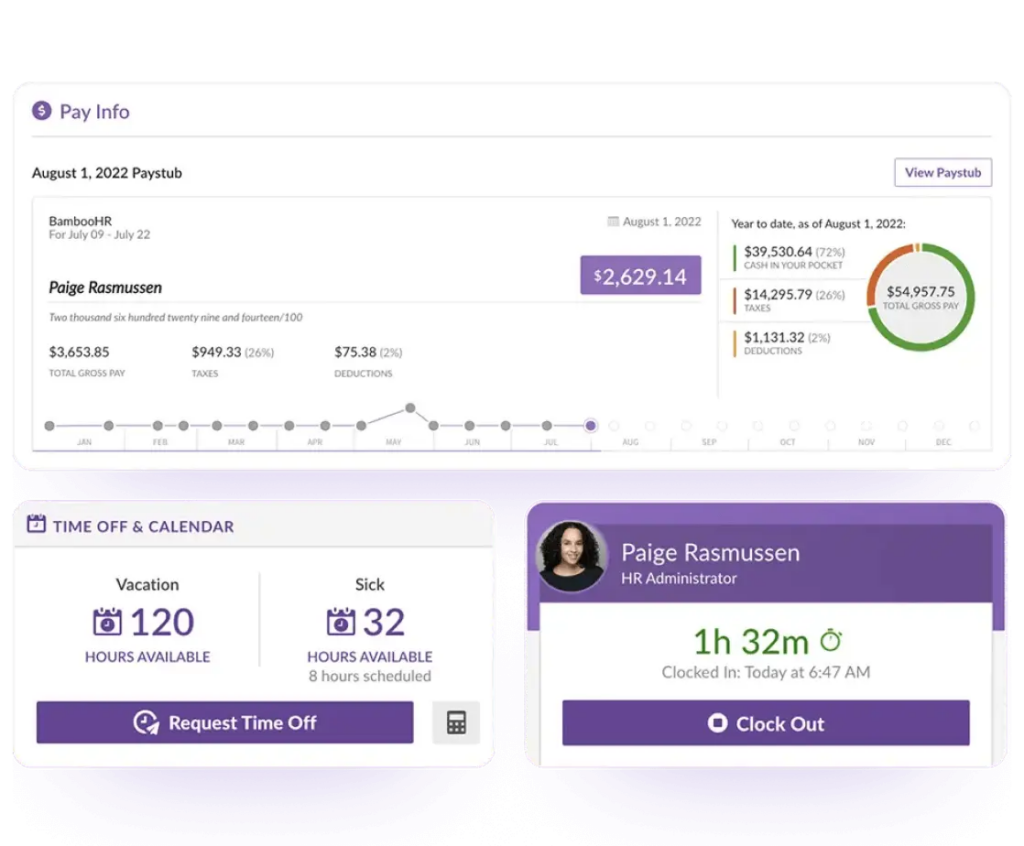
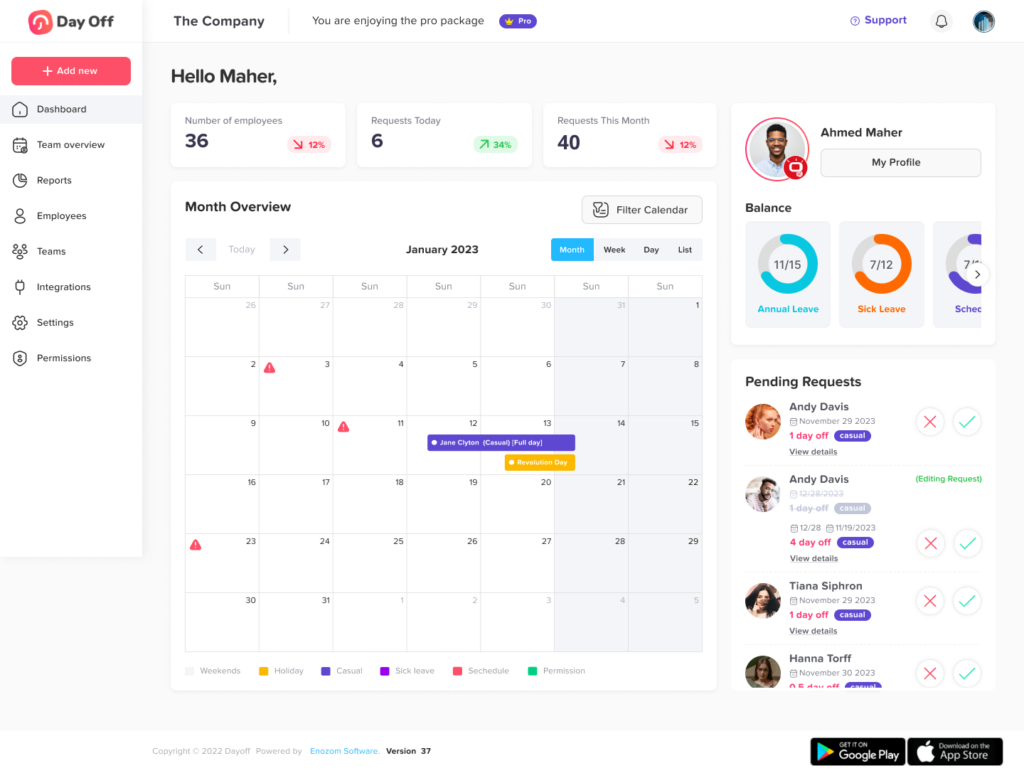
A practical example of technology serving the part-time workforce is Day Off, an innovative tool designed to simplify the management of PTO and other leave types. This platform can be particularly beneficial for businesses looking to streamline their PTO policies for part time employees. By offering a centralized system for tracking leave requests and balances, Day Off ensures that all employees have transparent access to their PTO information. It reduces the administrative workload on HR teams by automating the approval process and maintaining an accurate record of leave balances, thereby improving efficiency and employee satisfaction.

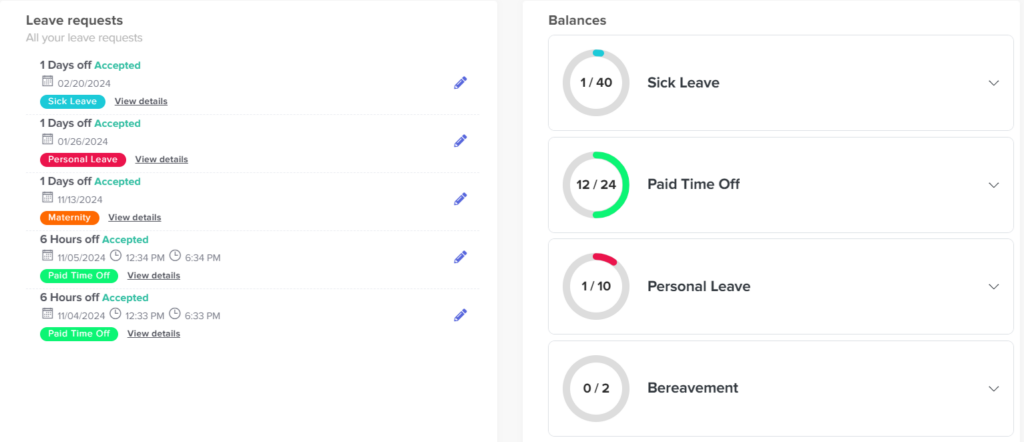
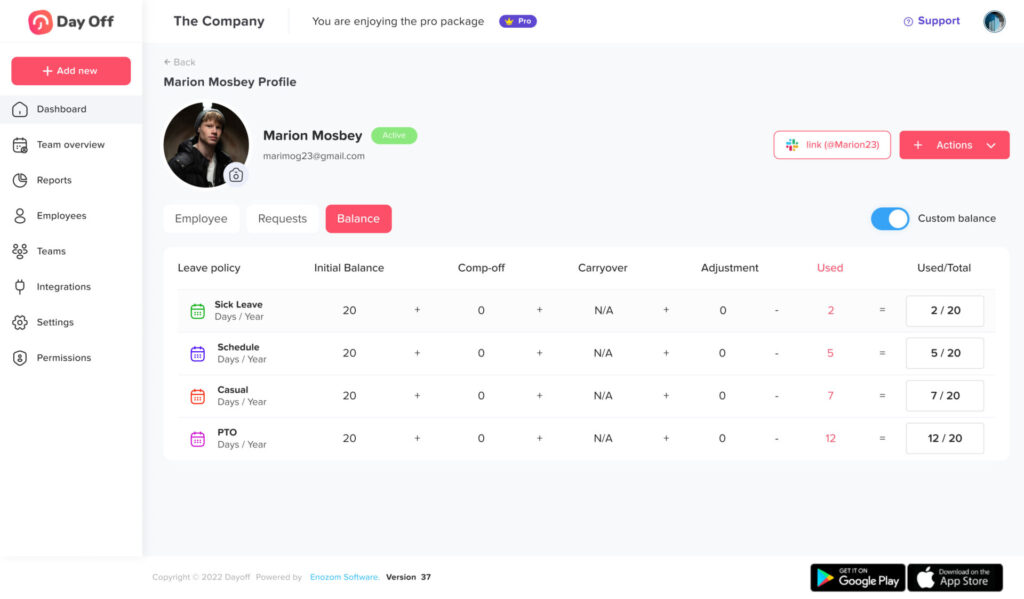
Easy Tracking and PTO Management
One of the big hurdles in handling benefits for part-time staff is keeping an accurate tab on work hours to guarantee they get the right amount of paid time off (PTO). The old way of doing things often led to mistakes and took a lot of time. Now, automated systems like Day Off are changing the game. These smart systems are great at keeping track of PTO based on the rules of the company. With Day Off, fairness and clarity in handing out PTO are a given, which is super important for keeping employees happy and feeling valued.
Direct Control with Self-Service
Day Off also brings to the table self-service portals, a big leap forward. These online spaces let employees handle and see how much PTO they have, all with a few clicks. This sense of control is a big boost for part-time staff, making them feel more connected to their benefits. It also makes life easier for HR teams, cutting down on the paperwork and questions they have to deal with.
Boosting Efficiency and Cutting Down Mistakes
Bringing technology into the mix for benefits management does wonders for making things run smoother. With Day Off, the process of assigning benefits and calculating PTO is automated, which means fewer mistakes and sticking to the rules without a hitch. Plus, Day Off can analyze data and give reports, helping HR folks get better at offering benefits and meeting the unique needs of part-time staff.

Day Off is all about making it easier to manage PTO and benefits for part-time employees. By automating the boring stuff and giving employees the reins to manage their own benefits, Day Off helps companies run more smoothly and keeps part-time workers feeling respected and looked after.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Are part-time employees legally entitled to paid time off (PTO)?
No, federal law does not require employers to provide PTO to either full-time or part-time employees. However, many employers voluntarily offer PTO to part-time workers as a competitive advantage in attracting and retaining talent. Eligibility and accrual policies are set by each employer.
How is PTO typically calculated for part-time employees?
PTO for part-time employees is generally calculated based on the number of hours worked. Common methods include:
-
Prorated Allocation: Part-time employees receive a portion of the PTO provided to full-time employees, based on their average weekly hours.
-
Hourly Accrual: Employees earn PTO in real time as they work, for example, accruing one hour of PTO for every 30 hours worked, ensuring fairness regardless of schedule.
Can part-time employees qualify for health insurance?
Yes, in some cases. Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), employers with 50 or more full-time equivalent employees must offer health insurance to those working 30 or more hours per week. Some employers also voluntarily extend health coverage to part-time employees below this threshold, depending on their internal policies and benefits structure.
Do part-time employees get access to retirement plans?
Often, yes. Many employers offer part-time employees access to retirement plans like 401(k)s, especially once certain criteria are met, such as completing a specific tenure or working a minimum number of hours per year. Recent legislative changes are also expanding access to retirement benefits for part-time workers.
What other benefits might part-time employees receive?
In addition to PTO and health insurance, part-time employees may be eligible for:
-
Dental and vision insurance
-
Employee assistance programs (EAPs)
-
Tuition reimbursement or training access
-
Employee discounts and perks
-
Flexible work arrangements and schedules
Benefit eligibility often depends on hours worked and company policy.
How does technology like Day Off help manage PTO for part-time employees?
Day Off simplifies leave management by automating PTO calculations based on work schedules, ensuring that part-time employees receive accurate and fair leave allocations. It reduces manual tracking errors, offers real-time visibility into leave balances, and streamlines the request and approval process, making it easier for both employees and HR teams to stay aligned.
Is it difficult to manage PTO for part-time staff without a tool like Day Off?
Yes, managing PTO manually can be time-consuming and prone to inconsistencies, especially for part-time roles with variable hours. Day Off eliminates these challenges by automating accruals, aligning PTO with scheduled hours, and providing centralized tracking. This not only ensures compliance but also boosts efficiency and transparency.
Can employees view and request PTO directly through Day Off?
Absolutely. Day Off features a user-friendly self-service portal where employees can log in to check their current leave balances, submit time-off requests, and track approvals, all in real time. This empowers part-time employees to manage their benefits while reducing HR’s administrative burden.
Why is offering PTO to part-time employees important?
Providing PTO to part-time employees fosters a sense of inclusion and respect, reinforcing that all team members, regardless of hours worked, are valued. It supports work-life balance, enhances job satisfaction, and strengthens employee loyalty, all of which contribute to a healthier, more committed workforce.
Conclusion:
As the workforce continues to evolve, with a growing emphasis on flexibility and part-time employment, the role of technology in managing benefits becomes increasingly critical. Tools like Day Off exemplify how technological solutions can address the unique challenges of administering part time benefits. By leveraging such advancements, companies can not only enhance their operational efficiency but also significantly improve the work experience for their part-time employees, making them feel valued and supported.